8.2 Bones of the Upper Limb
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Describe the bones of the upper limb, including the bones of the arm, forearm, wrist, and hand
- Appropriately name the regions of the upper limb and list the bones in each region
- List the bones and bony landmarks that articulate at each joint of the upper limb
The upper limb is divided into three regions. These consist of the arm, located between the shoulder and elbow joints; the forearm, which is between the elbow and wrist joints; and the hand, which is located distal to the wrist. There are 30 bones in each upper limb. The humerus is the single bone of the arm, and the ulna (medially) and the radius (laterally) are the paired bones of the forearm. The base of the hand contains eight carpal bones, and the palm of the hand is formed by five metacarpal bones. The fingers and thumb contain a total of 14 phalanges.
Humerus
The humerus is the single bone of the arm region (Figure 8.2.1). At its proximal end is the head of the humerus. This is the large, round, smooth region that faces medially. The head articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula to form the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint (see Chapter 9). The margin of the smooth area of the head is the anatomical neck of the humerus. Located on the lateral side of the proximal humerus is an expanded bony area called the greater tubercle. The smaller lesser tubercle of the humerus is found on the anterior aspect of the humerus. Both the greater and lesser tubercles serve as attachment sites for muscles that act across the shoulder joint (see Chapter 11). Passing between the greater and lesser tubercles is the narrow intertubercular groove (sulcus), which is also known as the bicipital groove because it provides passage for a tendon of the biceps brachii muscle. The surgical neck is located where the proximal end of the humerus joins the narrow shaft of the humerus, and is a common site of arm fractures. The deltoid tuberosity is a roughened, V-shaped region located on the lateral side in the middle of the humerus shaft. As its name indicates, it is the site of attachment for the deltoid muscle.
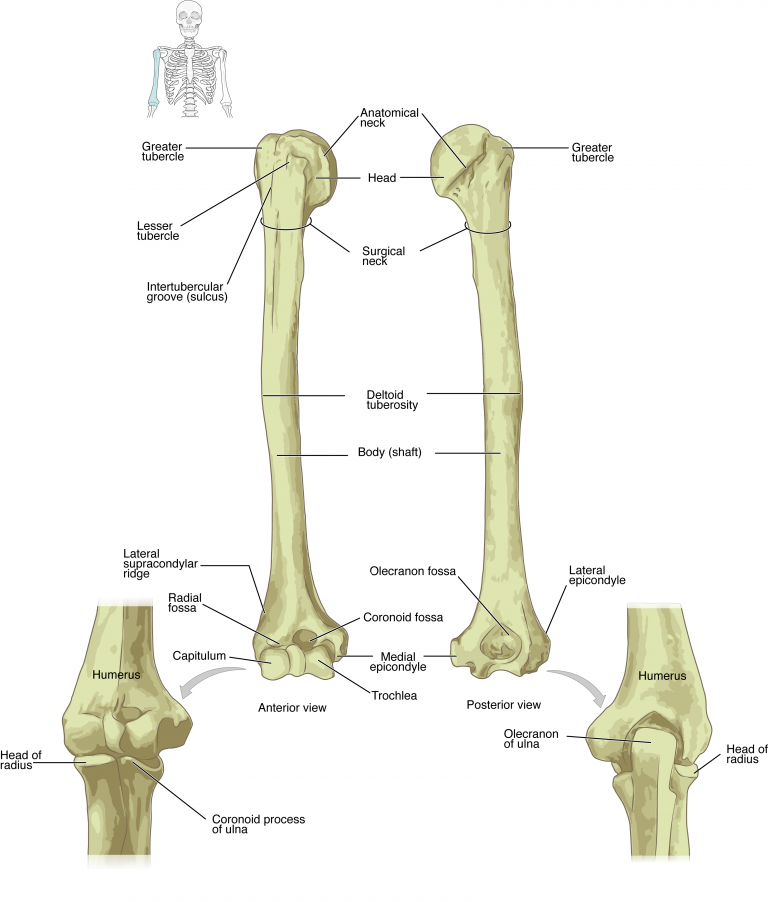
Distally, the humerus becomes flattened. The prominent bony projection on the medial side is the medial epicondyle of the humerus. The much smaller lateral epicondyle of the humerus is found on the lateral side of the distal humerus. The roughened ridge of bone above the lateral epicondyle is the lateral supracondylar ridge. All of these areas are attachment points for muscles that act on the forearm, wrist, and hand. The powerful grasping muscles of the anterior forearm arise from the medial epicondyle, which is thus larger and more robust than the lateral epicondyle that gives rise to the weaker posterior forearm muscles (see Chapter 11).
The distal end of the humerus has two articulation areas, which join the ulna and radius bones of the forearm to form the elbow joint. The more medial of these areas is the trochlea, a spindle- or pulley-shaped region (trochlea = “pulley”), which articulates with the ulna bone. Immediately lateral to the trochlea is the capitulum (“small head”), a knob-like structure located on the anterior surface of the distal humerus. The capitulum articulates with the radius bone of the forearm. Just above these bony areas are two small depressions. These spaces accommodate the forearm bones when the elbow is fully bent (flexed). Superior to the trochlea is the coronoid fossa, which receives the coronoid process of the ulna, and superior to the capitulum is the radial fossa, which receives the head of the radius when the elbow is flexed. Similarly, the posterior humerus has the olecranon fossa, a larger depression that receives the olecranon process of the ulna when the forearm is fully extended.
Ulna
The ulna is the medial bone of the forearm. It runs parallel to the radius, which is the lateral bone of the forearm (Figure 8.2.2). The proximal end of the ulna resembles a crescent wrench with its large, C-shaped, trochlear notch. This region articulates with the trochlea of the humerus as part of the elbow joint. The inferior margin of the trochlear notch is formed by a prominent lip of bone called the coronoid process of the ulna. Just below this on the anterior ulna is a roughened area called the ulnar tuberosity. To the lateral side and slightly inferior to the trochlear notch is a small, smooth area called the radial notch of the ulna. This area is the site of articulation between the proximal ends of the radius and ulna, forming the proximal radioulnar joint. The posterior and superior portions of the proximal ulna make up the olecranon process, which forms the bony tip of the elbow.
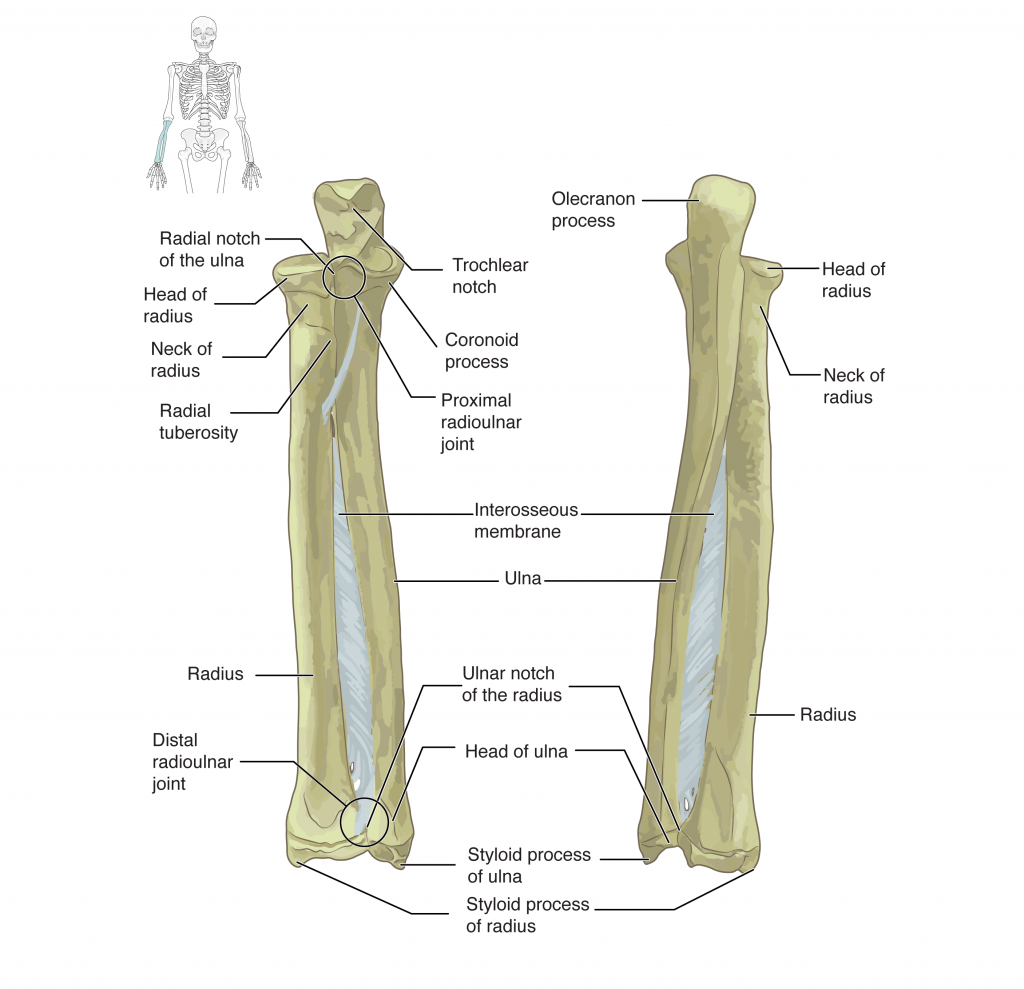
More distal is the shaft of the ulna. The lateral side of the shaft forms a ridge called the interosseous border of the ulna. This is the line of attachment for the interosseous membrane of the forearm, a sheet of dense connective tissue that unites the ulna and radius bones. The small, rounded area that forms the distal end is the head of the ulna. Projecting from the posterior side of the ulnar head is the styloid process of the ulna, a short bony projection. This serves as an attachment point for connective tissues that unite the distal end of the ulna with the carpal bones of the wrist joint.
In the anatomical position, with the elbow fully extended and the palms facing forward, the arm and forearm do not form a straight line. Instead, the forearm deviates laterally by 5–15 degrees from the line of the arm. This deviation is called the carrying angle. It allows the forearm and hand to swing freely or to carry an object without hitting the hip. The carrying angle is larger in females.
Radius
The radius runs parallel to the ulna, on the lateral (thumb) side of the forearm (see Figure 8.2.2). The head of the radius is a disc-shaped structure that forms the proximal end. The small depression on the surface of the head articulates with the capitulum of the humerus as part of the elbow joint, whereas the smooth, outer margin of the head articulates with the radial notch of the ulna at the proximal radioulnar joint. The neck of the radius is the narrowed region immediately below the expanded head. Inferior to this point on the medial side is the radial tuberosity, an oval-shaped, bony protuberance that serves as a muscle attachment point. The shaft of the radius is slightly curved and has a small ridge along its medial side. This ridge forms the interosseous border of the radius, which, like the similar border of the ulna, is the line of attachment for the interosseous membrane that unites the two forearm bones. The distal end of the radius has a smooth surface for articulation with two carpal bones to form the radiocarpal joint or wrist joint (Figure 8.2.3 and Figure 8.2.4). On the medial side of the distal radius is the ulnar notch of the radius. This shallow depression articulates with the head of the ulna, which together form the distal radioulnar joint. The lateral end of the radius has a pointed projection called the styloid process of the radius. This provides attachment for ligaments that support the lateral side of the wrist joint. Compared to the styloid process of the ulna, the styloid process of the radius projects more distally, thereby limiting the range of movement for lateral deviations of the hand at the wrist joint.
External Website

Watch this video to see how fractures of the distal radius bone can affect the wrist joint. Explain the problems that may occur if a fracture of the distal radius involves the joint surface of the radiocarpal joint of the wrist.
Carpal Bones
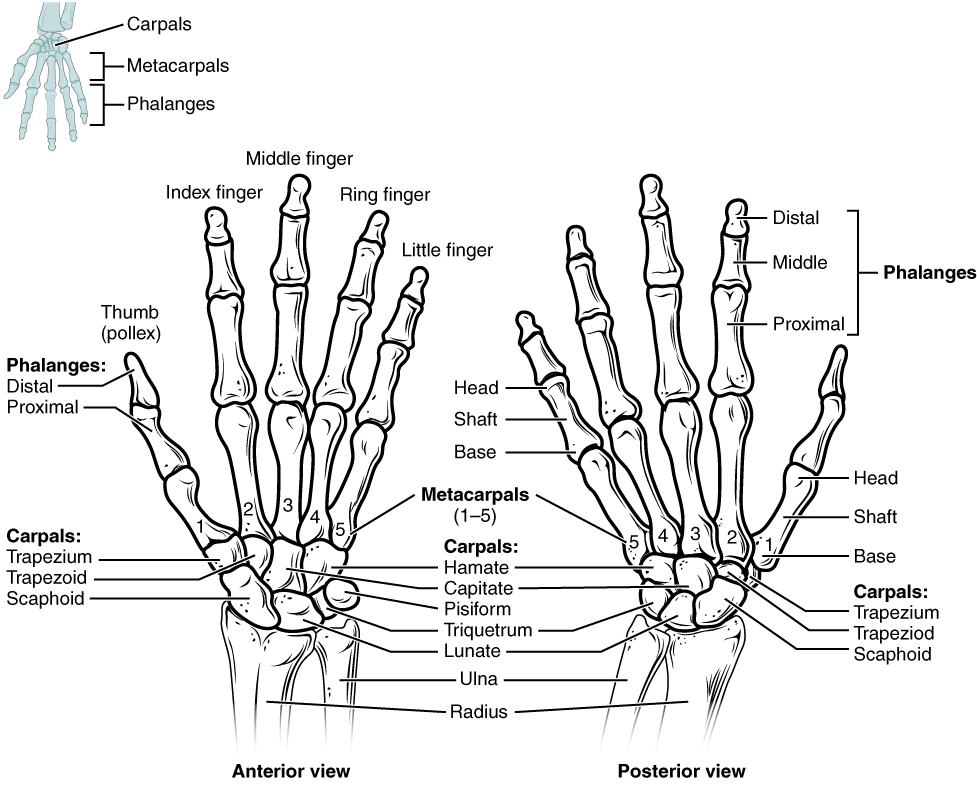
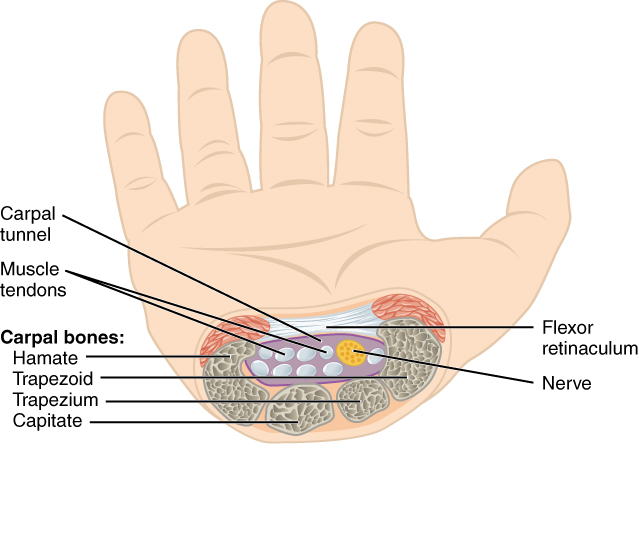
The wrist and base of the hand are formed by a series of eight small carpal bones (see Figure 8.2.3). The carpal bones are arranged in two rows, forming a proximal row of four carpal bones and a distal row of four carpal bones. The bones in the proximal row, running from the lateral (thumb) side to the medial side, are the scaphoid (“boat-shaped”), lunate (“moon-shaped”), triquetrum (“three-cornered”), and pisiform (“pea-shaped”) bones. The small, rounded pisiform bone articulates with the anterior surface of the triquetrum bone. The pisiform thus projects anteriorly, where it forms the bony bump that can be felt at the medial base of your hand. The distal bones (lateral to medial) are the trapezium (“table”), trapezoid (“resembles a table”), capitate (“head-shaped”), and hamate (“hooked bone”) bones. The hamate bone is characterized by a prominent bony extension on its anterior side called the hook of the hamate bone.
A helpful mnemonic for remembering the arrangement of the carpal bones is “So Long To Pinky, Here Comes The Thumb.” This mnemonic starts on the lateral side and names the proximal bones from lateral to medial (scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform), then makes a U-turn to name the distal bones from medial to lateral (hamate, capitate, trapezoid, trapezium). Thus, it starts and finishes on the lateral side.
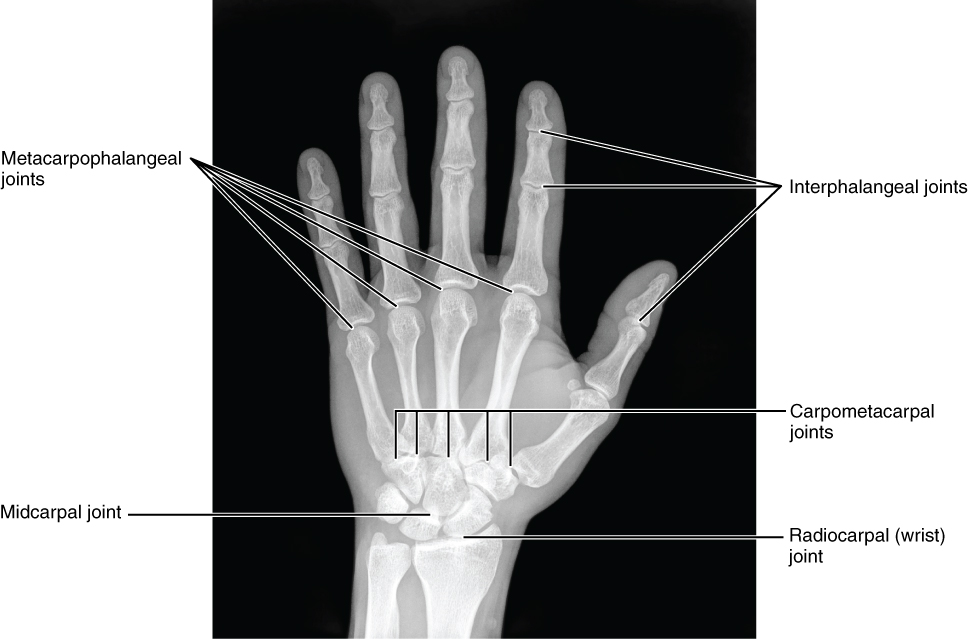
The carpal bones form the base of the hand. This can be seen in the radiograph (X-ray image) of the hand that shows the relationships of the hand bones to the skin creases of the hand (see Figure 8.2.4). Within the carpal bones, the four proximal bones are united to each other by ligaments to form a unit. Only three of these bones, the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum, contribute to the radiocarpal joint. The scaphoid and lunate bones articulate directly with the distal end of the radius, whereas the triquetrum bone articulates with a fibrocartilaginous pad (creating a space in the X-ray in Figure 8.2.4 between the ulna and the triquetrum). The distal end of the ulna thus does not directly articulate with any of the carpal bones.
The four distal carpal bones are also held together as a group by ligaments. The proximal and distal rows of carpal bones articulate with each other to form the midcarpal joint (see Figure 8.2.4). Together, the radiocarpal and midcarpal joints are responsible for all movements of the hand at the wrist. The distal carpal bones also articulate with the metacarpal bones of the hand.
In the articulated hand, the carpal bones form a U-shaped grouping. A strong ligament called the flexor retinaculum spans the top of this U-shaped area to maintain this grouping of the carpal bones (Figure 8.2.5). The flexor retinaculum is attached laterally to the trapezium and scaphoid bones, and medially to the hamate and pisiform bones. Together, the carpal bones and the flexor retinaculum form a passageway called the carpal tunnel, with the carpal bones forming the walls and floor, and the flexor retinaculum forming the roof of this space. The tendons of nine muscles of the anterior forearm and an important nerve (the median nerve) pass through this narrow tunnel to enter the hand. Overuse of the muscle tendons or wrist injury can produce inflammation and swelling within this space. This produces compression of the nerve, resulting in carpal tunnel syndrome, which is characterized by pain or numbness, and muscle weakness in those areas of the hand supplied by this nerve.
Metacarpal Bones
The palm of the hand contains five elongated metacarpal bones. These bones lie between the carpal bones of the wrist and the bones of the fingers and thumb (see Figure 8.2.3). The proximal end of each metacarpal bone articulates with one of the distal carpal bones. Each of these articulations is a carpometacarpal joint (see Figure 8.2.4). The expanded distal end of each metacarpal bone articulates at the metacarpophalangeal joint with the proximal phalanx bone of the thumb or one of the fingers. The distal end also forms the knuckles of the hand, at the base of the fingers. The metacarpal bones are numbered 1–5, beginning at the thumb.
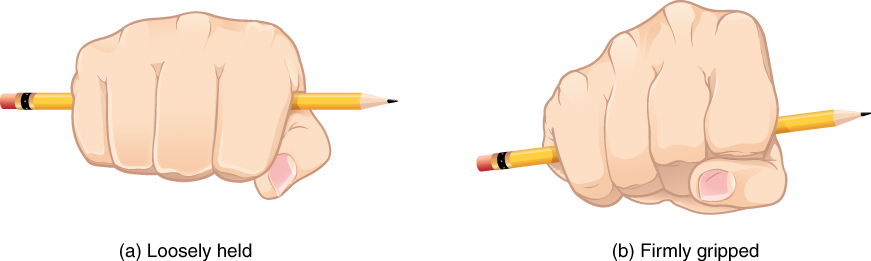
The first metacarpal bone, at the base of the thumb, is separated from the other metacarpal bones. This allows it a freedom of motion that is independent of the other metacarpal bones, which is very important for thumb mobility. The remaining metacarpal bones are united together to form the palm of the hand. The second and third metacarpal bones are firmly anchored in place and are immobile. However, the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones have limited anterior-posterior mobility, a motion that is greater for the fifth bone. This mobility is important during power gripping with the hand (Figure 8.2.6). The anterior movement of these bones, particularly the fifth metacarpal bone, increases the strength of contact for the medial hand during gripping actions.
Phalanx Bones
The fingers and thumb contain 14 bones, each of which is called a phalanx bone (plural = phalanges), named after the ancient Greek phalanx (a rectangular block of soldiers). The thumb (pollex) is digit number 1 and has two phalanges, a proximal phalanx, and a distal phalanx bone (see Figure 8.2.3). Digits 2 (index finger) through 5 (little finger) have three phalanges each, called the proximal, middle, and distal phalanx bones. An interphalangeal joint is one of the articulations between adjacent phalanges of the digits (see Figure 8.2.4).
External Website

Visit this site to explore the bones and joints of the hand. What are the three arches of the hand, and what is the importance of these during the gripping of an object?
Disorders of the…Appendicular System: Fractures of Upper Limb Bones
Due to our constant use of the hands and the rest of our upper limbs, an injury to any of these areas will cause a significant loss of functional ability. Many fractures result from a hard fall onto an outstretched hand. The resulting transmission of force up the limb may result in a fracture of the humerus, radius, or scaphoid bones. These injuries are especially common in elderly people whose bones are weakened due to osteoporosis.
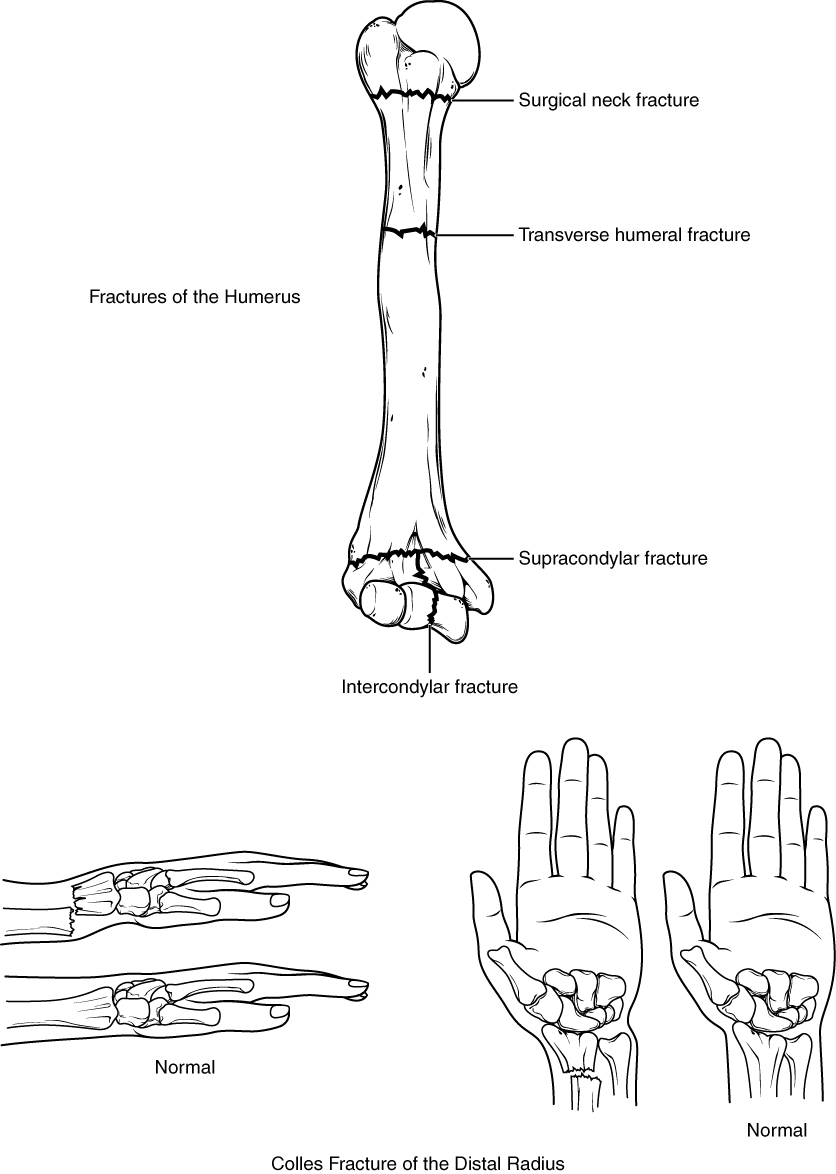
Falls onto the hand or elbow, or direct blows to the arm, can result in fractures of the humerus (Figure 8.2.7). Following a fall, fractures at the surgical neck, the region at which the expanded proximal end of the humerus joins with the shaft, can result in an impacted fracture, in which the distal portion of the humerus is driven into the proximal portion. Falls or blows to the arm can also produce transverse or spiral fractures of the humeral shaft.
In children, a fall onto the tip of the elbow frequently results in a distal humerus fracture. In these, the olecranon of the ulna is driven upward, resulting in a fracture across the distal humerus, above both epicondyles (supracondylar fracture), or a fracture between the epicondyles, thus separating one or both of the epicondyles from the body of the humerus (intercondylar fracture). With these injuries, the immediate concern is possible compression of the artery to the forearm due to swelling of the surrounding tissues. If compression occurs, the resulting ischemia (lack of oxygen) due to reduced blood flow can quickly produce irreparable damage to the forearm muscles.
Another frequent injury following a fall onto an outstretched hand is a Colles fracture (“col-lees”) of the distal radius (see Figure 8.2.7). This involves a complete transverse fracture across the distal radius that drives the separated distal fragment of the radius posteriorly and superiorly. This injury results in a characteristic “dinner fork” bend of the forearm just above the wrist due to the posterior displacement of the hand. This is the most frequent forearm fracture and is a common injury in persons over the age of 50, particularly in older women with osteoporosis. It also commonly occurs following a high-speed fall onto the hand during activities such as snowboarding or skating.
The most commonly fractured carpal bone is the scaphoid, often resulting from a fall onto the hand. Deep pain at the lateral wrist may yield an initial diagnosis of a wrist sprain, but a radiograph taken several weeks after the injury, after tissue swelling has subsided, will reveal the fracture. Due to the poor blood supply to the scaphoid bone, healing will be slow and there is the danger of bone necrosis and subsequent degenerative joint disease of the wrist.
External Website

Watch this video to learn about a Colles fracture, a break of the distal radius, usually caused by falling onto an outstretched hand. When would surgery be required and how would the fracture be repaired in this case?
Chapter Review
Each upper limb is divided into three regions and contains a total of 30 bones. The arm is the region located between the shoulder and elbow joints. This area contains the humerus. The proximal humerus consists of the head, which articulates with the scapula at the glenohumeral joint, the greater and lesser tubercles separated by the intertubercular (bicipital) groove, and the anatomical and surgical necks. The humeral shaft has the roughened area of the deltoid tuberosity on its lateral side. The distal humerus is flattened, forming a lateral supracondylar ridge that terminates at the small lateral epicondyle. The medial side of the distal humerus has the large, medial epicondyle. The articulating surfaces of the distal humerus consist of the trochlea medially and the capitulum laterally. Depressions on the humerus that accommodate the forearm bones during bending (flexing) and straightening (extending) of the elbow include the coronoid fossa, the radial fossa, and the olecranon fossa.
The forearm is the region of the upper limb located between the elbow and wrist joints. This region contains two bones, the ulna medially and the radius on the lateral (thumb) side. The elbow joint is formed by the articulation between the trochlea of the humerus and the trochlear notch of the ulna, plus the articulation between the capitulum of the humerus and the head of the radius. The proximal radioulnar joint is the articulation between the head of the radius and the radial notch of the ulna. The proximal ulna also has the olecranon process, forming an expanded posterior region, and the coronoid process and ulnar tuberosity on its anterior aspect. On the proximal radius, the narrowed region below the head is the neck; distal to this is the radial tuberosity. The shaft portions of both the ulna and radius have an interosseous border, whereas the distal ends of each bone have a pointed styloid process. The distal radioulnar joint is found between the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch of the radius. The distal end of the radius articulates with the proximal carpal bones, but the ulna does not.
The base of the hand is formed by eight carpal bones. The carpal bones are united into two rows of bones. The proximal row contains (from lateral to medial) the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform bones. Specifically, the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum bones contribute to the formation of the radiocarpal joint. The distal row of carpal bones contains (from medial to lateral) the hamate, capitate, trapezoid, and trapezium bones. The proximal and distal carpal rows articulate with each other at the midcarpal joint. The carpal bones, together with the flexor retinaculum, also form the carpal tunnel of the wrist.
The five metacarpal bones form the palm of the hand. The metacarpal bones are numbered 1–5, starting with the thumb side. The first metacarpal bone is freely mobile, but the other bones are united as a group. The digits are also numbered 1–5, with the thumb being number 1. The fingers and thumb contain a total of 14 phalanges (phalanx bones). The thumb contains a proximal and a distal phalanx, whereas the remaining digits each contain proximal, middle, and distal phalanges.
Interactive Link Questions
Watch this video to see how fractures of the distal radius bone can affect the wrist joint. Explain the problems that may occur if a fracture of the distal radius involves the joint surface of the radiocarpal joint of the wrist.
A fracture through the joint surface of the distal radius may make the articulating surface of the radius rough or jagged. This can then cause painful movements involving this joint and the early development of arthritis. Surgery can return the joint surface to its original smoothness, thus allowing for the return of normal function.
Visit this site to explore the bones and joints of the hand. What are the three arches of the hand, and what is the importance of these during the gripping of an object?
The hand has a proximal transverse arch, a distal transverse arch, and a longitudinal arch. These allow the hand to conform to objects being held. These arches maximize the amount of surface contact between the hand and object, which enhances stability and increases sensory input.
Watch this video to learn about a Colles fracture, a break of the distal radius, usually caused by falling onto an outstretched hand. When would surgery be required and how would the fracture be repaired in this case?
Surgery may be required if the fracture is unstable, meaning that the broken ends of the radius won’t stay in place to allow for proper healing. In this case, metal plates and screws can be used to stabilize the fractured bone.
Review Questions
Critical Thinking Questions
1. Your friend runs out of gas and you have to help push his car. Discuss the sequence of bones and joints that convey the forces passing from your hand, through your upper limb and your pectoral girdle, and to your axial skeleton.
2. Describe the features of the human hand that allows us to manipulate small objects with precision. Be as detailed about the bone and joints as you can.
Glossary
- anatomical neck
- line on the humerus located around the outside margin of the humeral head
- arm
- region of the upper limb located between the shoulder and elbow joints; contains the humerus bone
- bicipital groove
- intertubercular groove; narrow groove located between the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus
- capitate
- from the lateral side, the third of the four distal carpal bones; articulates with the scaphoid and lunate proximally, the trapezoid laterally, the hamate medially, and primarily with the third metacarpal distally
- capitulum
- knob-like bony structure located anteriorly on the lateral, distal end of the humerus
- carpal bone
- one of the eight small bones that form the wrist and base of the hand; these are grouped as a proximal row consisting of (from lateral to medial) the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform bones, and a distal row containing (from lateral to medial) the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate bones
- carpal tunnel
- passageway between the anterior forearm and hand formed by the carpal bones and flexor retinaculum
- carpometacarpal joint
- articulation between one of the carpal bones in the distal row and a metacarpal bone of the hand
- coronoid fossa
- depression on the anterior surface of the humerus above the trochlea; this space receives the coronoid process of the ulna when the elbow is maximally flexed
- coronoid process of the ulna
- projecting bony lip located on the anterior, proximal ulna; forms the inferior margin of the trochlear notch
- deltoid tuberosity
- roughened, V-shaped region located laterally on the mid-shaft of the humerus
- distal radioulnar joint
- articulation between the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch of the radius
- elbow joint
- joint located between the upper arm and forearm regions of the upper limb; formed by the articulations between the trochlea of the humerus and the trochlear notch of the ulna, and the capitulum of the humerus and the head of the radius
- flexor retinaculum
- strong band of connective tissue at the anterior wrist that spans the top of the U-shaped grouping of the carpal bones to form the roof of the carpal tunnel
- forearm
- region of the upper limb located between the elbow and wrist joints; contains the radius and ulna bones
- greater tubercle
- enlarged prominence located on the lateral side of the proximal humerus
- hamate
- from the lateral side, the fourth of the four distal carpal bones; articulates with the lunate and triquetrum proximally, the fourth and fifth metacarpals distally, and the capitate laterally
- hand
- region of the upper limb distal to the wrist joint
- head of the humerus
- smooth, rounded region on the medial side of the proximal humerus; articulates with the glenoid fossa of the scapula to form the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint
- head of the radius
- disc-shaped structure that forms the proximal end of the radius; articulates with the capitulum of the humerus as part of the elbow joint, and with the radial notch of the ulna as part of the proximal radioulnar joint
- head of the ulna
- small, rounded distal end of the ulna; articulates with the ulnar notch of the distal radius, forming the distal radioulnar joint
- hook of the hamate bone
- bony extension located on the anterior side of the hamate carpal bone
- humerus
- single bone of the upper arm
- interosseous border of the radius
- narrow ridge located on the medial side of the radial shaft; for attachment of the interosseous membrane between the ulna and radius bones
- interosseous border of the ulna
- narrow ridge located on the lateral side of the ulnar shaft; for attachment of the interosseous membrane between the ulna and radius
- interosseous membrane of the forearm
- sheet of dense connective tissue that unites the radius and ulna bones
- interphalangeal joint
- articulation between adjacent phalanx bones of the hand or foot digits
- intertubercular groove (sulcus)
- bicipital groove; narrow groove located between the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus
- lateral epicondyle of the humerus
- small projection located on the lateral side of the distal humerus
- lateral supracondylar ridge
- narrow, bony ridge located along the lateral side of the distal humerus, superior to the lateral epicondyle
- lesser tubercle
- small, bony prominence located on anterior side of the proximal humerus
- lunate
- from the lateral side, the second of the four proximal carpal bones; articulates with the radius proximally, the capitate and hamate distally, the scaphoid laterally, and the triquetrum medially
- medial epicondyle of the humerus
- enlarged projection located on the medial side of the distal humerus
- metacarpal bone
- one of the five long bones that form the palm of the hand; numbered 1–5, starting on the lateral (thumb) side of the hand
- metacarpophalangeal joint
- articulation between the distal end of a metacarpal bone of the hand and a proximal phalanx bone of the thumb or a finger
- midcarpal joint
- articulation between the proximal and distal rows of the carpal bones; contributes to movements of the hand at the wrist
- neck of the radius
- narrowed region immediately distal to the head of the radius
- olecranon fossa
- large depression located on the posterior side of the distal humerus; this space receives the olecranon process of the ulna when the elbow is fully extended
- olecranon process
- expanded posterior and superior portions of the proximal ulna; forms the bony tip of the elbow
- phalanx bone of the hand
- (plural = phalanges) one of the 14 bones that form the thumb and fingers; these include the proximal and distal phalanges of the thumb, and the proximal, middle, and distal phalanx bones of the fingers two through five
- pisiform
- from the lateral side, the fourth of the four proximal carpal bones; articulates with the anterior surface of the triquetrum
- pollex
- (also, thumb) digit 1 of the hand
- proximal radioulnar joint
- articulation formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the head of the radius
- radial fossa
- small depression located on the anterior humerus above the capitulum; this space receives the head of the radius when the elbow is maximally flexed
- radial notch of the ulna
- small, smooth area on the lateral side of the proximal ulna; articulates with the head of the radius as part of the proximal radioulnar joint
- radial tuberosity
- oval-shaped, roughened protuberance located on the medial side of the proximal radius
- radiocarpal joint
- wrist joint, located between the forearm and hand regions of the upper limb; articulation formed proximally by the distal end of the radius and the fibrocartilaginous pad that unites the distal radius and ulna bone, and distally by the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum carpal bones
- radius
- bone located on the lateral side of the forearm
- scaphoid
- from the lateral side, the first of the four proximal carpal bones; articulates with the radius proximally, the trapezoid, trapezium, and capitate distally, and the lunate medially
- shaft of the humerus
- narrow, elongated, central region of the humerus
- shaft of the radius
- narrow, elongated, central region of the radius
- shaft of the ulna
- narrow, elongated, central region of the ulna
- styloid process of the radius
- pointed projection located on the lateral end of the distal radius
- styloid process of the ulna
- short, bony projection located on the medial end of the distal ulna
- surgical neck
- region of the humerus where the expanded, proximal end joins with the narrower shaft
- trapezium
- from the lateral side, the first of the four distal carpal bones; articulates with the scaphoid proximally, the first and second metacarpals distally, and the trapezoid medially
- trapezoid
- from the lateral side, the second of the four distal carpal bones; articulates with the scaphoid proximally, the second metacarpal distally, the trapezium laterally, and the capitate medially
- triquetrum
- from the lateral side, the third of the four proximal carpal bones; articulates with the lunate laterally, the hamate distally, and has a facet for the pisiform
- trochlea
- pulley-shaped region located medially at the distal end of the humerus; articulates at the elbow with the trochlear notch of the ulna
- trochlear notch
- large, C-shaped depression located on the anterior side of the proximal ulna; articulates at the elbow with the trochlea of the humerus
- ulna
- bone located on the medial side of the forearm
- ulnar notch of the radius
- shallow, smooth area located on the medial side of the distal radius; articulates with the head of the ulna at the distal radioulnar joint
- ulnar tuberosity
- roughened area located on the anterior, proximal ulna inferior to the coronoid process
Solutions
Answers for Critical Thinking Questions
- As you push against the car, forces will pass from the metacarpal bones of your hand into the carpal bones at the base of your hand. Forces will then pass through the midcarpal and radiocarpal joints into the radius and ulna bones of the forearm. These will pass the force through the elbow joint into the humerus of the arm, and then through the glenohumeral joint into the scapula. The force will travel through the acromioclavicular joint into the clavicle, and then through the sternoclavicular joint into the sternum, which is part of the axial skeleton.
- The human hand is able to manipulate small objects due to the relatively small size of the bones of the wrist and hand, and the large number of joints, which provides for precise movements.
This work, Anatomy & Physiology, is adapted from Anatomy & Physiology by OpenStax, licensed under CC BY. This edition, with revised content and artwork, is licensed under CC BY-SA except where otherwise noted.
Images, from Anatomy & Physiology by OpenStax, are licensed under CC BY except where otherwise noted.
Access the original for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction.

