11.5 Axial muscles of the abdominal wall and thorax
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Identify the following muscles and give their origins, insertions, actions and innervations:
- Axial muscles of the abdominal wall and thorax
AXIAL MUSCLES OF THE ABDOMINAL WALL AND THORAX
It is a complex job to balance the body on two feet and walk upright. The muscles of the vertebral column, thorax, and abdominal wall extend, flex, and stabilize different parts of the body’s trunk. The deep muscles of the body’s core help maintain posture as well as provide stability for movement of the limbs.
Muscles of the Abdomen
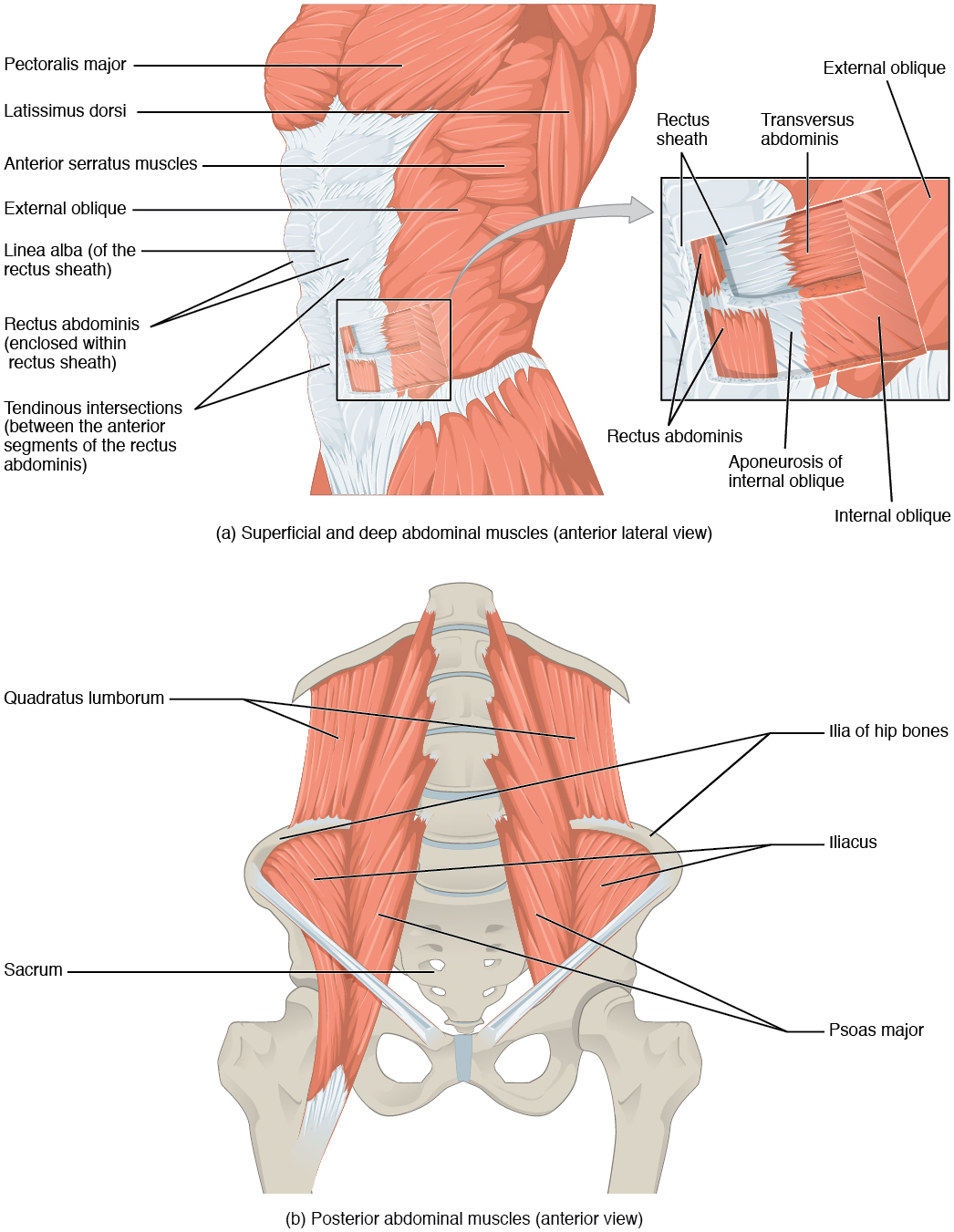
There are four pairs of abdominal muscles that make up the abdominal wall: the rectus abdominis, the external abdominal obliques, the internal abdominal obliques and the transverse abdominis (Figure 11.4.9 and Table 11.6).
| Muscles of the Abdomen (Table 11.6) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Prime mover | Origin | Insertion |
| Twisting at waist; also bending to the side | Vertebral column | Supination; lateral flexion | External obliques; internal obliques | Ribs 5–12; ilium | Ribs 7–10; linea alba; ilium |
| Squeezing abdomen during forceful exhalations, defecation, urination, and childbirth | Abdominal cavity | Compression | Transversus abdominus | Ilium; ribs 5–10 | Sternum; linea alba; pubis |
| Sitting up | Vertebral column | Flexion | Rectus abdominis | Pubis | Sternum; ribs 5 and 7 |
| Bending to the side | Vertebral column | Lateral flexion | Quadratus lumborum | Ilium; ribs 5–10 | Rib 12; vertebrae L1–L4 |
Muscles of the Abdomen
| Prime mover | Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Origin | Insertion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| External obliques; internal obliques | Twisting at waist; also bending to the side | Vertebral column | Supination; lateral flexion | Ribs 5–12; ilium | Ribs 7–10; linea alba; ilium |
| Transversus abdominus | Squeezing abdomen during forceful exhalations, defecation, urination, and childbirth | Abdominal cavity | Compression | Ilium; ribs 5–10 | Sternum; linea alba; pubis |
| Rectus abdominis | Sitting up | Vertebral column | Flexion | Pubis | Sternum; ribs 5 and 7 |
| Quadratus lumborum | Bending to the side | Vertebral column | Lateral flexion | Ilium; ribs 5–10 | Rib 12; vertebrae L1–L4 |
There are three flat skeletal muscles in the antero-lateral wall of the abdomen. The external oblique, closest to the surface, extend inferiorly and medially, in the direction of sliding one’s four fingers into pants pockets. Perpendicular to it is the intermediate internal oblique, extending superiorly and medially, the direction the thumbs usually go when the other fingers are in the pants pocket. The deep muscle, the transverse abdominis, is arranged transversely around the abdomen, similar to a belt. This arrangement of three bands of muscles in different orientations allows various movements and rotations of the trunk. The three layers of muscle also help to protect the internal abdominal organs in an area where there is no bone.
The linea alba is a white, fibrous band that is made of the bilateral rectus sheaths (see Figure 11.4.9) that join at the anterior midline of the body. These enclose the rectus abdominis muscles that originate at the pubic crest and symphysis, and extend the length of the body’s trunk. Each muscle is segmented by three transverse bands of collagen fibers called the tendinous intersections resulting in the look of “six-pack abs”.
The posterior abdominal wall is formed by the lumbar vertebrae, parts of the ilia of the hip bones, psoas major and iliacus muscles, and quadratus lumborum muscle. This part of the core plays a key role in stabilizing the rest of the body and maintaining posture.
Career Connection – Physical Therapists
Those who have a muscle or joint injury will most likely be sent to a physical therapist (PT) after seeing their regular doctor. PTs have a master’s degree or doctorate, and are highly trained experts in the mechanics of body movements. Many PTs also specialize in sports injuries.
If you injured your shoulder while you were kayaking, the first thing a physical therapist would do during your first visit is assess the functionality of the joint. The range of motion of a particular joint refers to the normal movements the joint performs. The PT will ask you to abduct and adduct, circumduct, and flex and extend the arm. The PT will note the shoulder’s degree of function, and based on the assessment of the injury, will create an appropriate physical therapy plan.
The first step in physical therapy will probably be applying a heat pack to the injured site, which acts much like a warm-up to draw blood to the area, to enhance healing. You will be instructed to do a series of exercises to continue the therapy at home, followed by icing, to decrease inflammation and swelling, which will continue for several weeks. When physical therapy is complete, the PT will do an exit exam and send a detailed report on the improved range of motion and return of normal limb function to your doctor. Gradually, as the injury heals, the shoulder will begin to function correctly. A PT works closely with patients to help them get back to their normal level of physical activity.
Muscles of the Thorax
The muscles of the chest serve to facilitate breathing by changing the volume of the thoracic cavity (Table 11.7). When you inhale your chest rises increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. Alternately, when you exhale, your chest falls decreasing the volume of the thoracic cavity.
| Muscles of the Thorax (Table 11.7) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Prime mover | Origin | Insertion |
| Inhalation; exhalation | Thoracic cavity | Compression; expansion | Diaphragm | Sternum; ribs 6–12; lumbar vertebrae | Central tendon |
| Inhalation;exhalation | Ribs | Elevation (expands thoracic cavity) | External intercostals | Rib superior to each intercostal muscle | Rib inferior to each intercostal muscle |
| Forced exhalation | Ribs | Movement along superior/inferior axis to bring ribs closer together | Internal intercostals | Rib inferior to each intercostal muscle | Rib superior to each intercostal muscle |
Muscles of the Thorax
| Prime mover | Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Origin | Insertion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diaphragm | Inhalation; exhalation | Thoracic cavity | Compression; expansion | Sternum; ribs 6–12; lumbar vertebrae | Central tendon |
| External intercostals | Inhalation;exhalation | Ribs | Elevation (expands thoracic cavity) | Rib superior to each intercostal muscle | Rib inferior to each intercostal muscle |
| Internal intercostals | Forced exhalation | Ribs | Movement along superior/inferior axis to bring ribs closer together | Rib inferior to each intercostal muscle | Rib superior to each intercostal muscle |
The Diaphragm
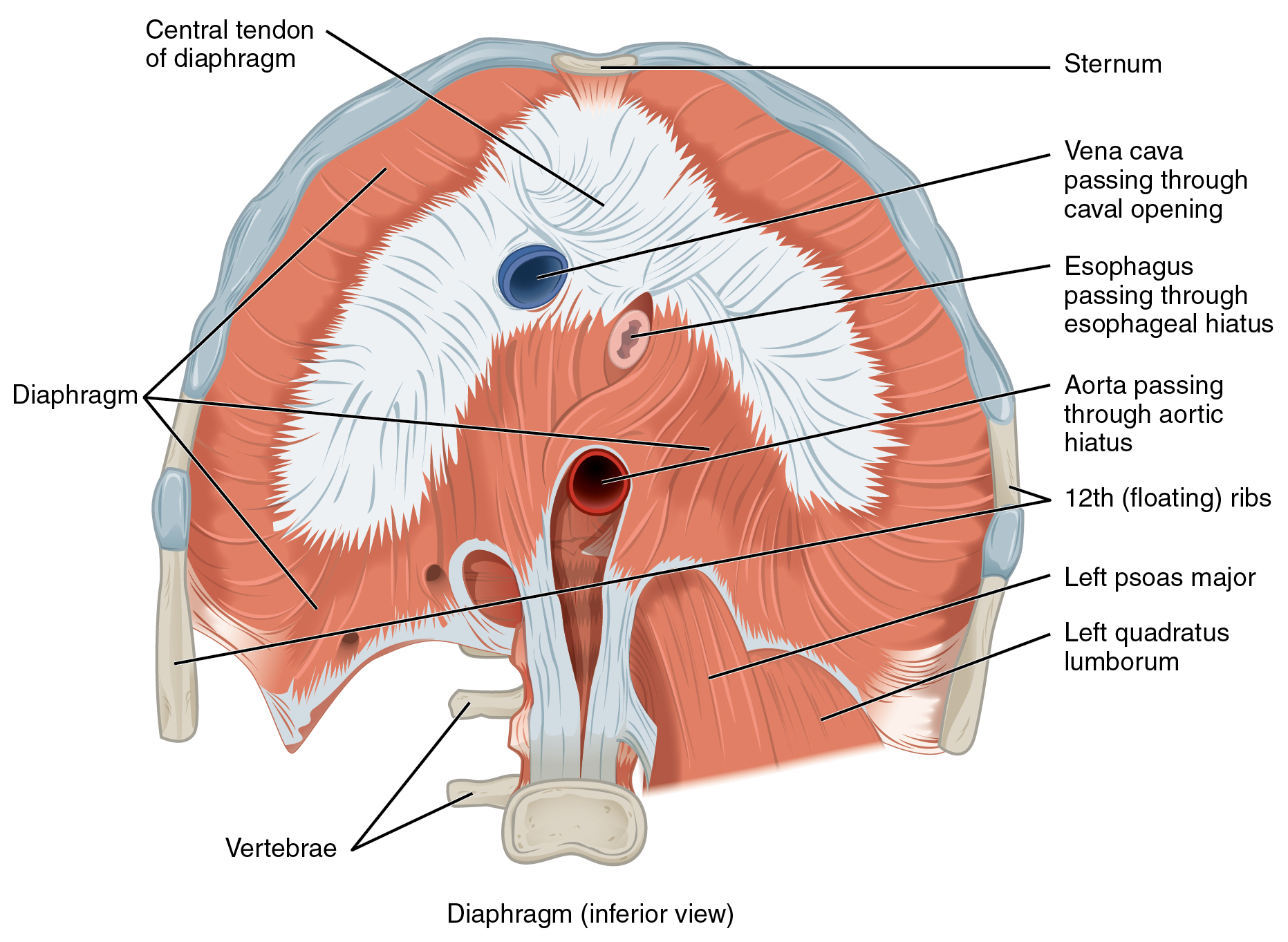
The change in volume of the thoracic cavity during breathing is due to the alternate contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm (Figure 11.4.10). It separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities, and is dome-shaped at rest. The superior surface of the diaphragm is convex, creating the elevated floor of the thoracic cavity. The inferior surface is concave, creating the curved roof of the abdominal cavity.
Defecating, urination, and even childbirth involve cooperation between the diaphragm and abdominal muscles (this cooperation is referred to as the “Valsalva maneuver”). While you hold your breath the diaphragm and abdominal muscles contract increasing the pressure of the peritoneal cavity and stabilizing the core. When the abdominal muscles contract, the pressure cannot push the diaphragm up, so it increases pressure on the intestinal tract (defecation), urinary tract (urination), or reproductive tract (childbirth).
The inferior surface of the pericardial sac and the inferior surfaces of the pleural membranes (parietal pleura) fuse onto the central tendon of the diaphragm. To the sides of the tendon are the skeletal muscle portions of the diaphragm, which insert into the tendon while having a number of origins including the xiphoid process of the sternum anteriorly, the inferior six ribs and their cartilages laterally, and the lumbar vertebrae and 12th ribs posteriorly.
The diaphragm also includes three openings for the passage of structures between the thorax and the abdomen. The inferior vena cava passes through the caval opening, and the esophagus and attached nerves pass through the esophageal hiatus. The aorta, thoracic duct, and azygous vein pass through the aortic hiatus of the posterior diaphragm.
The Intercostal Muscles
There are three sets of muscles, called intercostal muscles, which span each of the intercostal spaces. The principal role of the intercostal muscles is to assist in breathing by changing the dimensions of the rib cage (Figure 11.4.11).
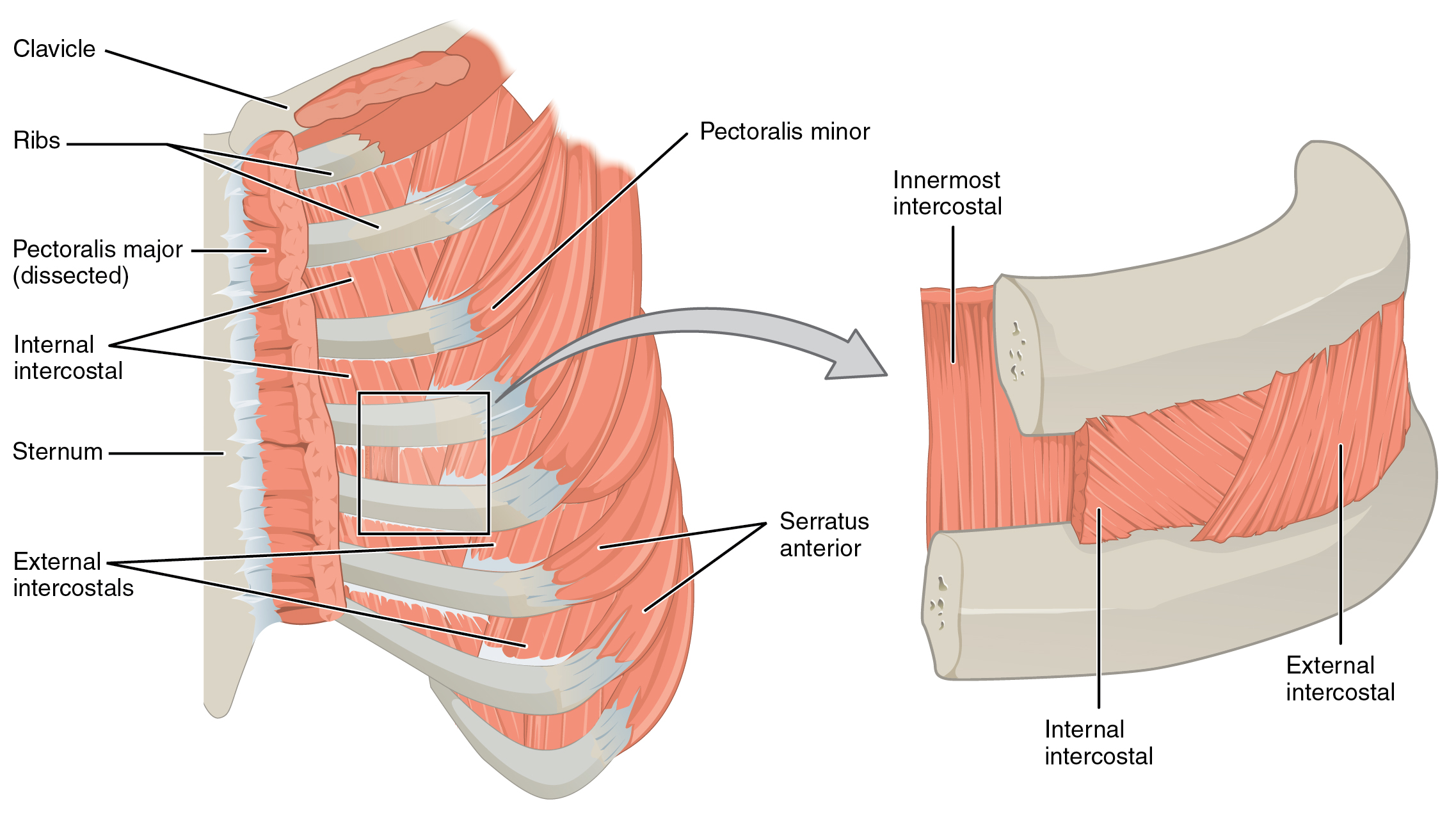
The 11 pairs of superficial external intercostal muscles aid in inspiration of air during breathing because when they contract, they raise the rib cage, which expands it. The 11 pairs of internal intercostal muscles, just under the externals, are used for expiration because they draw the ribs together to constrict the rib cage. The innermost intercostal muscles are the deepest, and they act as synergists for the action of the internal intercostals.
Muscles of the Pelvic Floor and Perineum
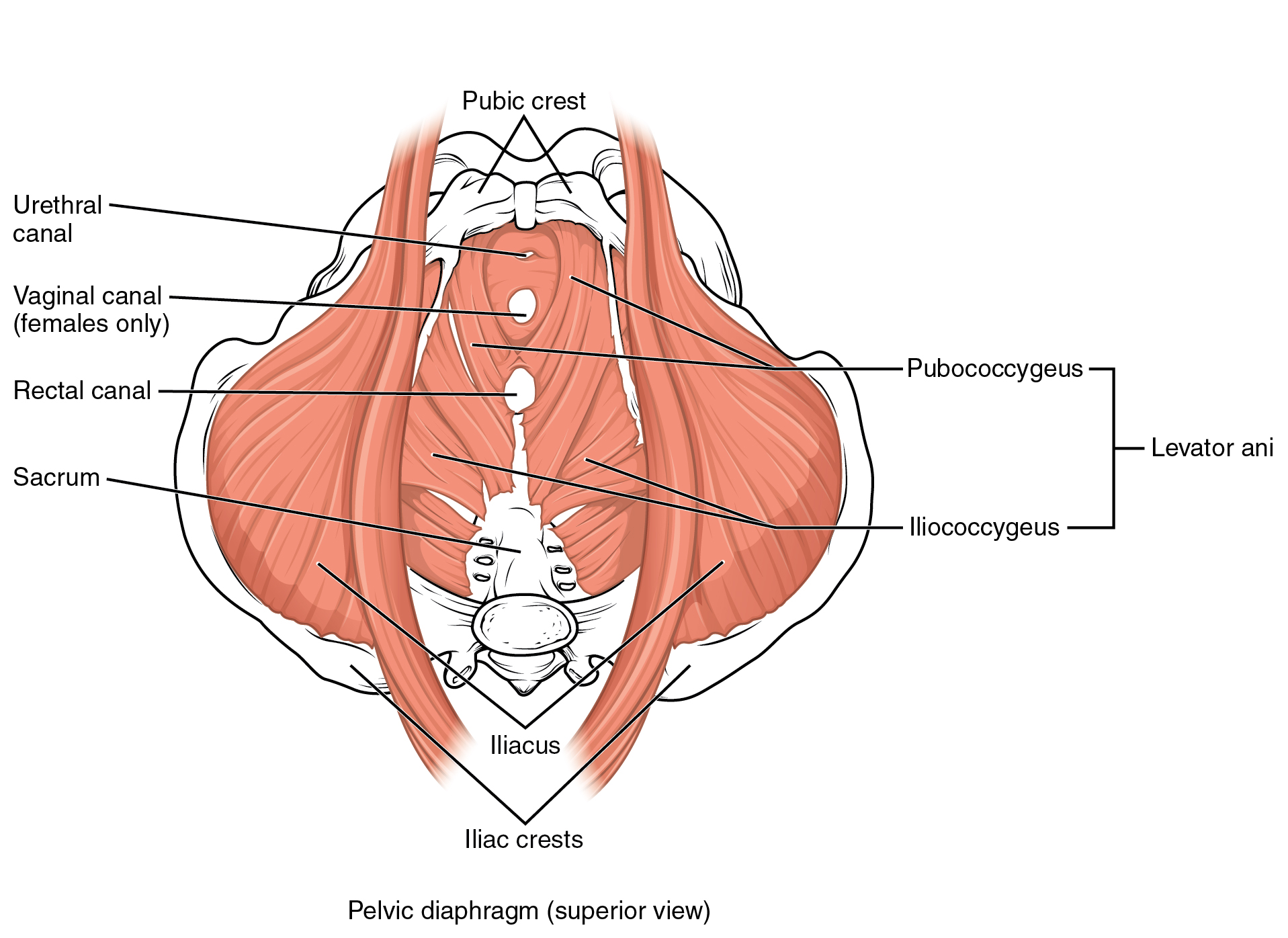
The pelvic floor (also referred to as the pelvic diaphragm) is a muscular sheet that defines the inferior portion of the pelvic cavity. The pelvic floor extends anteriorly to posteriorly from the pubis to the coccyx and is comprised of the levator ani and the ischiococcygeus. Its openings include the anal canal and urethra, and the vagina in women.
The large levator ani consists of two skeletal muscles, the pubococcygeus and the iliococcygeus (Figure 11.4.12). The levator ani is considered the most important muscle of the pelvic floor because it supports the pelvic viscera. It resists the pressure produced by contraction of the abdominal muscles so that the pressure is applied to the colon to aid in defecation and to the uterus to aid in childbirth (assisted by the ischiococcygeus, which pulls the coccyx anteriorly). This muscle also creates skeletal muscle sphincters at the urethra and anus.
The perineum is the diamond-shaped space between the pubic symphysis (anteriorly), the coccyx (posteriorly), and the ischial tuberosities (laterally), lying just inferior to the pelvic diaphragm (levator ani and ischiococcygeus). Divided transversely into triangles, the anterior is the urogenital triangle, which includes the external genitals and the posterior is the anal triangle containing the anus (Figure 11.4.13). The perineum is also divided into superficial and deep layers with some of the muscles common to men and women (Figure 11.4.14). Women also have the compressor urethrae and the sphincter urethrovaginalis, which function to close the vagina. In men, the deep transverse perineal muscle plays a role in ejaculation.
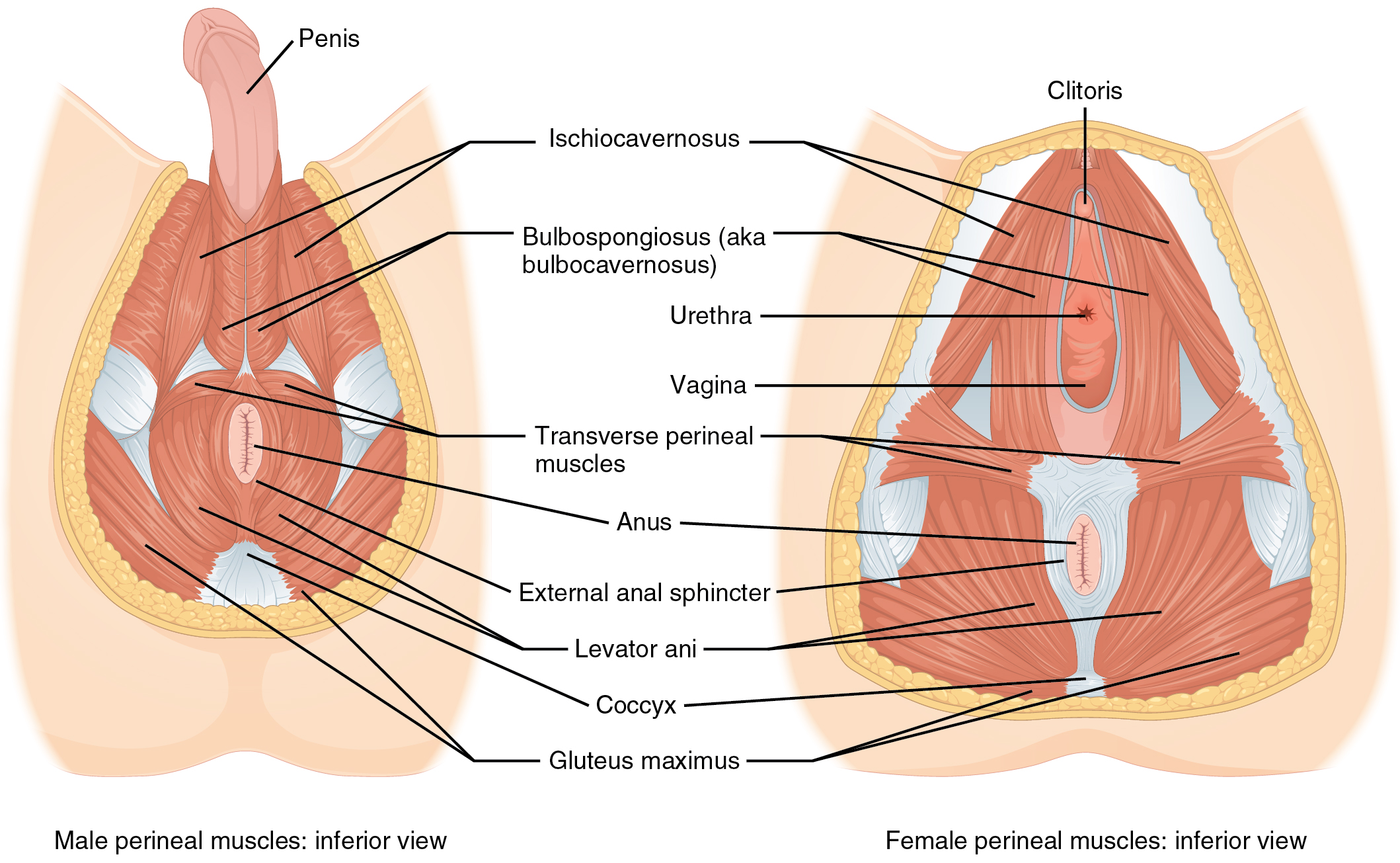
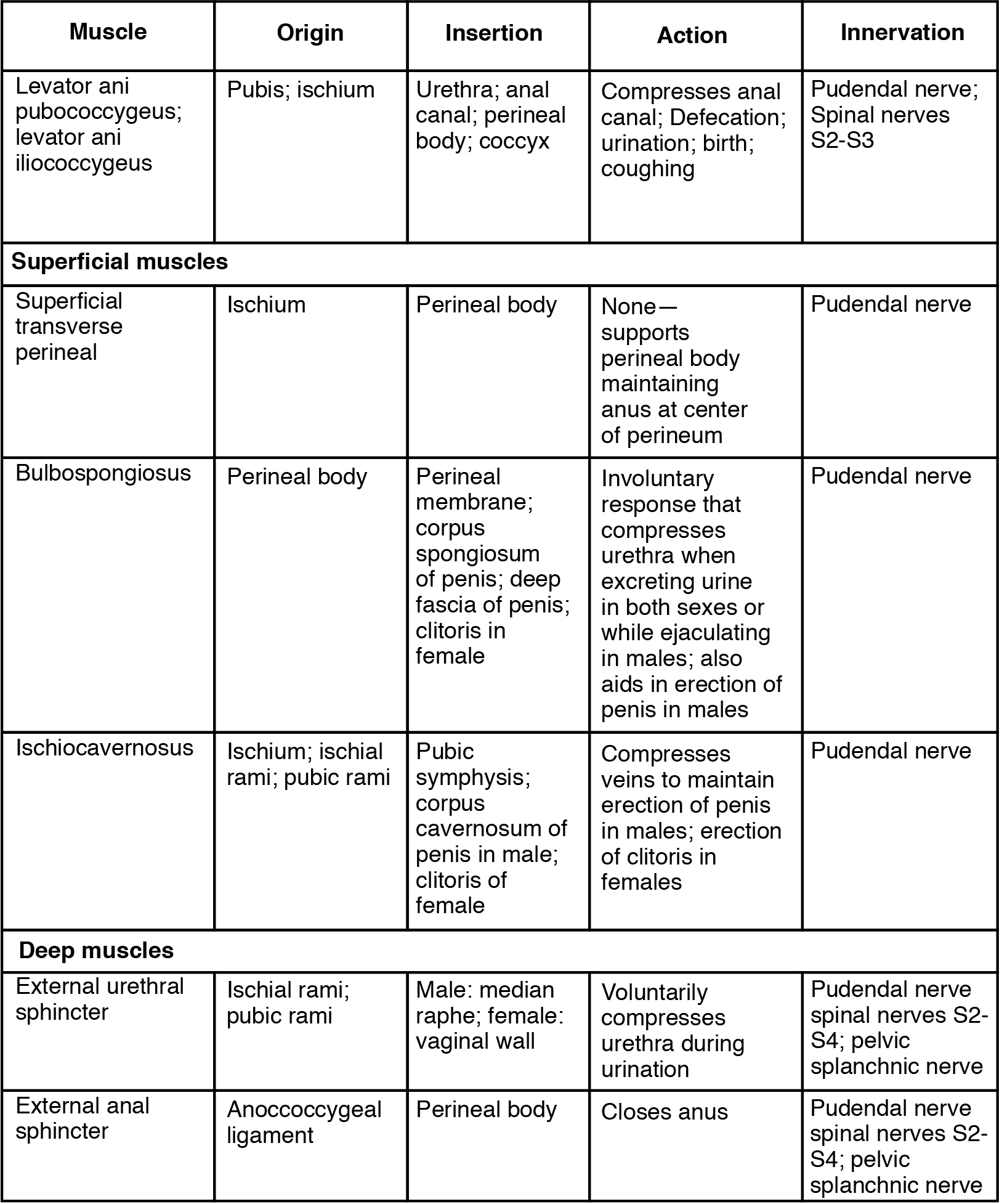
Muscles of the Perineum Common to Men and Women
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levator ani pubococcygeus; levator ani iliococcygeus | Pubis; ischium | Urethra; anal canal; perineal body; coccyx | Compresses anal canal; defecation; urination; birth; coughing | Pudendal nerve; Spinal nerves S2-S3 |
| Superficial muscles | ||||
| Superficial transverse perineal | Ischium | Perineal body | None- supports perineal body maintaining anus at center of perineum | Pudendal nerve |
| Bulbospongiosus | Perineal body | Perineal membrane; corpus spongiosum of penis; deep fascia of penis; clitoris in female | Involuntary response that compresses urethra when excreting urine in both sexes or while ejaculating in males; also aids in erection of penis in malse | Pudendal nerve |
| Ischiocavernosus | Ischium; ischial rami; pubic rami | Pubic symphysis; corpus cavernosum of penis in males; clitoris in females | Compresses veins to maintain erection of penis in males; erection of clitoris in females | Pudendal nerve |
| Deep muscles | ||||
| External urethral sphincter | Ischial rami; pubic rami | Male: median raphe; female: vaginal wall | Voluntarily compresses urethra during urination | Pudendal nerve spinal nerves S2-S4; pelvic splanchnic nerve |
| External anal sphincter | Anoccoccygeal ligament | Pernieal body | Closes anus | Pudendal nerve spinal nerves S2-S4; pelvic splanchnic nerve |
Chapter Review
Made of skin, fascia, and four pairs of muscle, the anterior abdominal wall protects the organs located in the abdomen and moves the vertebral column. These muscles include the rectus abdominis, which extends through the entire length of the trunk, the external oblique, the internal oblique, and the transversus abdominus. The quadratus lumborum forms the posterior abdominal wall.
The muscles of the thorax play a large role in breathing, especially the dome-shaped diaphragm. When it contracts and flattens, the volume inside the pleural cavities increases, which decreases the pressure within them. As a result, air will flow into the lungs. The external and internal intercostal muscles span the space between the ribs and help change the shape of the rib cage and the volume-pressure ratio inside the pleural cavities during inspiration and expiration.
The perineum muscles play roles in urination in both sexes, ejaculation in men, and vaginal contraction in women. The pelvic floor muscles support the pelvic organs, resist intra-abdominal pressure, and work as sphincters for the urethra, rectum, and vagina.
Review Questions
Critical Thinking Questions
- Describe the fascicle arrangement in the muscles of the abdominal wall. How do they relate to each other?
- What are some similarities and differences between the diaphragm and the pelvic diaphragm?
Glossary
- anal triangle
- posterior triangle of the perineum that includes the anus
- caval opening
- opening in the diaphragm that allows the inferior vena cava to pass through; foramen for the vena cava
- compressor urethrae
- deep perineal muscle in women
- deep transverse perineal
- deep perineal muscle in men
- diaphragm
- skeletal muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities and is dome-shaped at rest
- external intercostal
- superficial intercostal muscles that raise the rib cage
- external oblique
- superficial abdominal muscle with fascicles that extend inferiorly and medially
- iliococcygeus
- muscle that makes up the levator ani along with the pubococcygeus
- innermost intercostal
- the deepest intercostal muscles that draw the ribs together
- intercostal muscles
- muscles that span the spaces between the ribs
- internal intercostal
- muscles the intermediate intercostal muscles that draw the ribs together
- internal oblique
- flat, intermediate abdominal muscle with fascicles that run perpendicular to those of the external oblique
- ischiococcygeus
- muscle that assists the levator ani and pulls the coccyx anteriorly
- levator ani
- pelvic muscle that resists intra-abdominal pressure and supports the pelvic viscera
- linea alba
- white, fibrous band that runs along the midline of the trunk
- pelvic diaphragm
- muscular sheet that comprises the levator ani and the ischiococcygeus
- perineum
- diamond-shaped region between the pubic symphysis, coccyx, and ischial tuberosities
- pubococcygeus
- muscle that makes up the levator ani along with the iliococcygeus
- quadratus lumborum
- posterior part of the abdominal wall that helps with posture and stabilization of the body
- rectus abdominis
- long, linear muscle that extends along the middle of the trunk
- rectus sheaths
- tissue that makes up the linea alba
- sphincter urethrovaginalis
- deep perineal muscle in women
- tendinous intersections
- three transverse bands of collagen fibers that divide the rectus abdominis into segments
- transversus abdominis
- deep layer of the abdomen that has fascicles arranged transversely around the abdomen
- urogenital triangle
- anterior triangle of the perineum that includes the external genitals
Solutions
Answers for Critical Thinking Questions
- Tendons of the infraspinatus, supraspinatus, teres minor, and the subscapularis form the rotator cuff, which forms a foundation on which the arms and shoulders can be stabilized and move.
- The muscles that make up the shoulders and upper limbs include the muscles that position the pelvic girdle, the muscles that move the humerus, the muscles that move the forearm, and the muscles that move the wrists, hands, and fingers.
This work, Anatomy & Physiology, is adapted from Anatomy & Physiology by OpenStax, licensed under CC BY. This edition, with revised content and artwork, is licensed under CC BY-SA except where otherwise noted.
Images, from Anatomy & Physiology by OpenStax, are licensed under CC BY except where otherwise noted.
Access the original for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction.

