11.4 Axial Muscles of the Head Neck and Back
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Identify the following muscles and give their origins, insertions, actions and innervations:
- Axial muscles of the head neck and back
The skeletal muscles are divided into axial (muscles of the trunk and head) and appendicular (muscles of the arms and legs) categories. This system reflects the bones of the skeleton system, which are also arranged in this manner. Some of the axial muscles may seem to blur the boundaries because they cross over to the appendicular skeleton. The first grouping of the axial muscles you will review includes the muscles of the head and neck, then you will review the muscles of the vertebral column, and finally you will review the oblique and rectus muscles.
AXIAL MUSCLES OF THE HEAD NECK AND BACK
Muscles of Facial Expression
The muscles of facial expression originate from the surface of the skull or the fascia (connective tissue) of the face. The insertions of these muscles have fibers intertwined with connective tissue and the dermis of the skin. Because the muscles insert in the skin rather than on bone, when they contract, the skin moves to create facial expression (Figure 11.4.1).
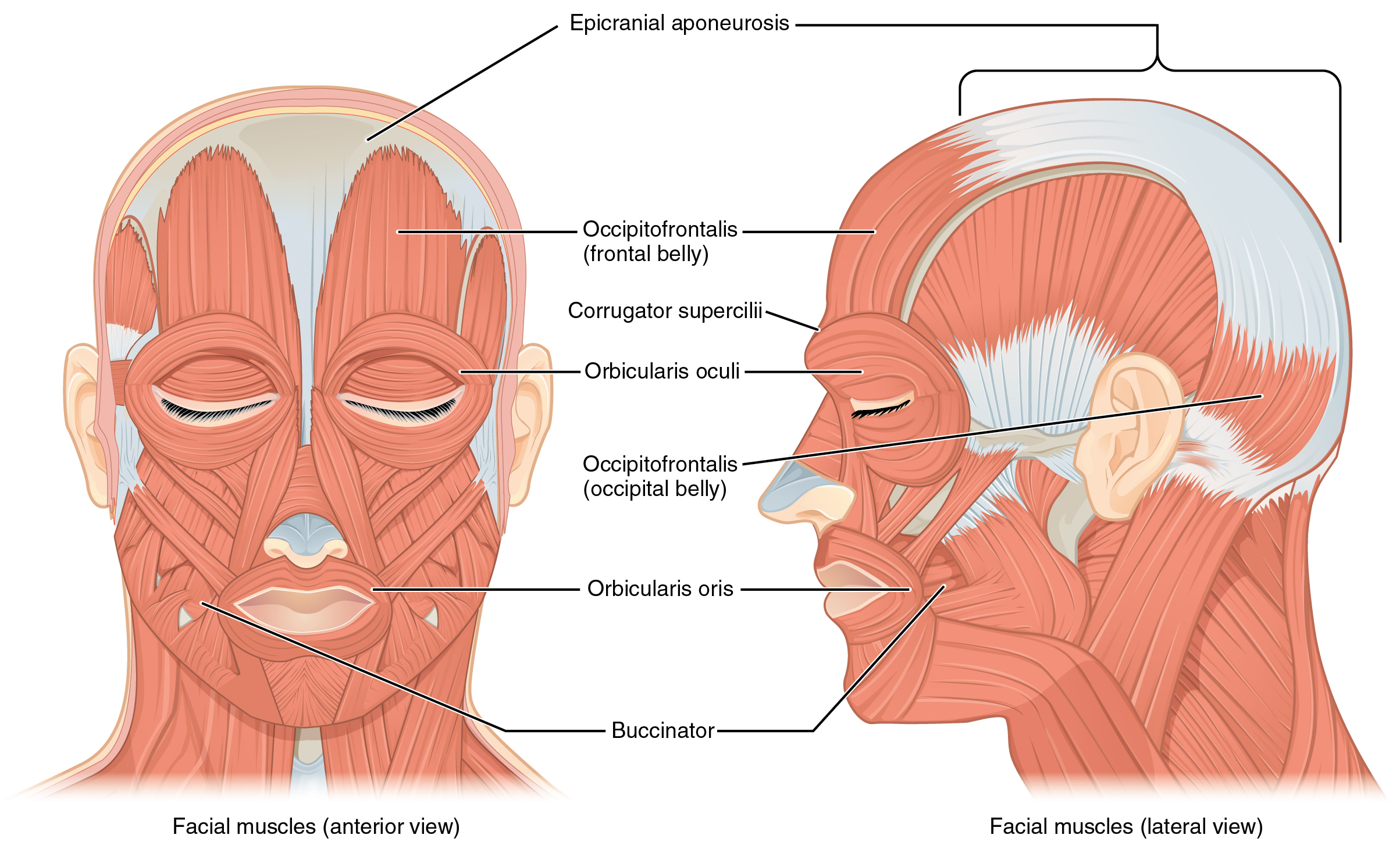
The orbicularis oris is a circular muscle that moves the lips, and the orbicularis oculi is a circular muscle that closes the eye. The occipitofrontalis muscle elevates the scalp and eyebrows. The muscle has a frontal belly and an occipital belly (near the occipital bone on the posterior part of the skull). In other words, there is a muscle on the forehead (frontalis) and one on the back of the head (occipitals). The two bellies are connected by a broad tendon called the epicranial aponeurosis, or galea aponeurosis (galea = “apple”). The physicians originally studying human anatomy thought the skull looked like an apple.
The buccinator muscle compresses the cheek. This muscle allows you to whistle, blow, and suck; and it contributes to the action of chewing. There are several small facial muscles, one of which is the corrugator supercilii, which is the prime mover of the eyebrows. Place your finger on your eyebrows at the point of the bridge of the nose. Raise your eyebrows as if you were surprised and lower your eyebrows as if you were frowning. With these movements, you can feel the action of the corrugator supercilli. Additional muscles of facial expression are presented in Figure 11.4.2.
Muscles That Move the Eyes
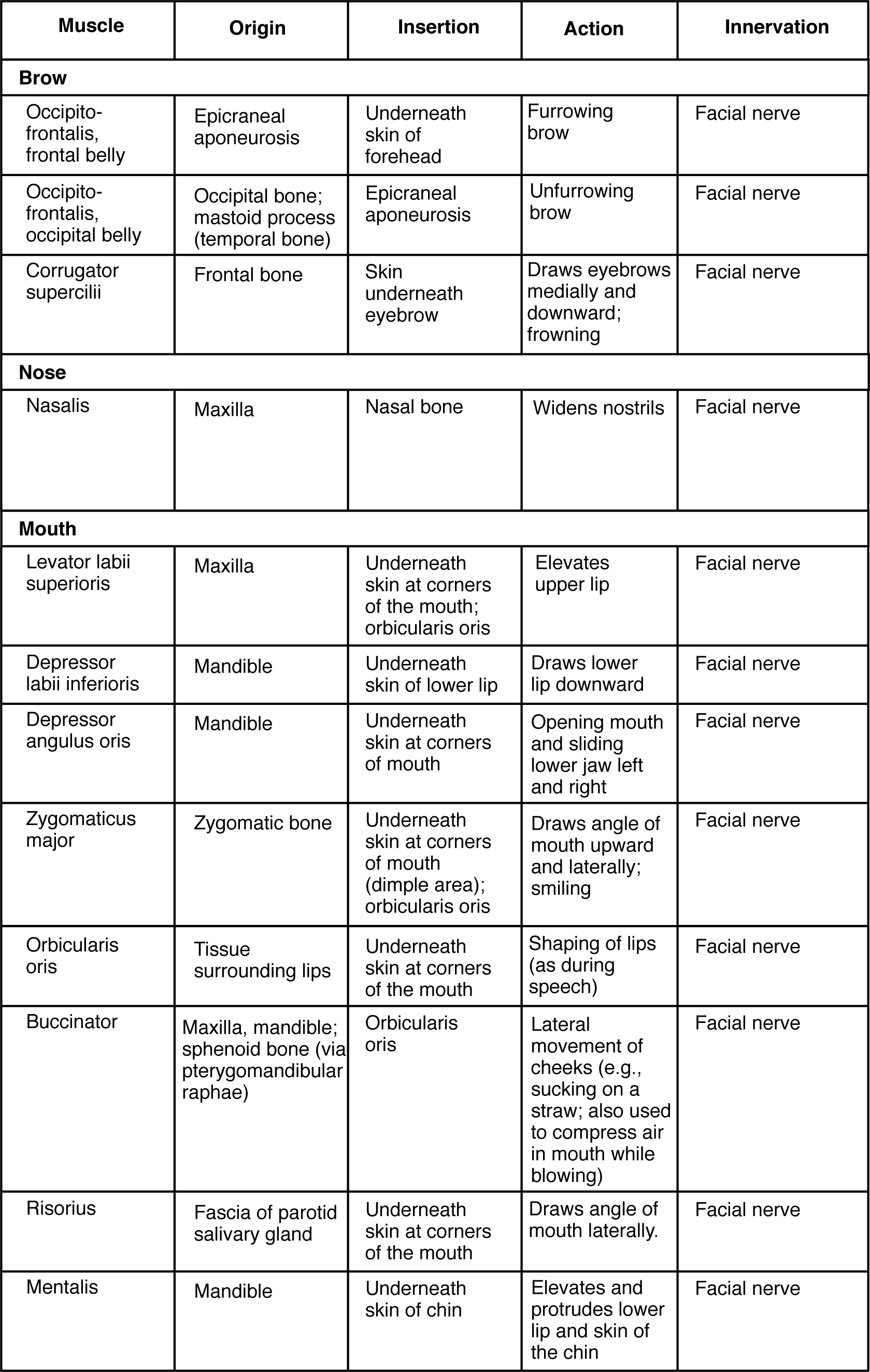
The movement of the eyeball is under the control of the extra ocular (extrinsic) eye muscles, which originate from the bones of the orbit and insert onto the outer surface of the white of the eye. These muscles are located inside the eye socket and cannot be seen on any part of the visible eyeball (Figure 11.4.3 and Table 11.3). If you have ever been to a doctor who held up a finger and asked you to follow it up, down, and to both sides, he or she is checking to make sure your eye muscles are acting in a coordinated pattern.
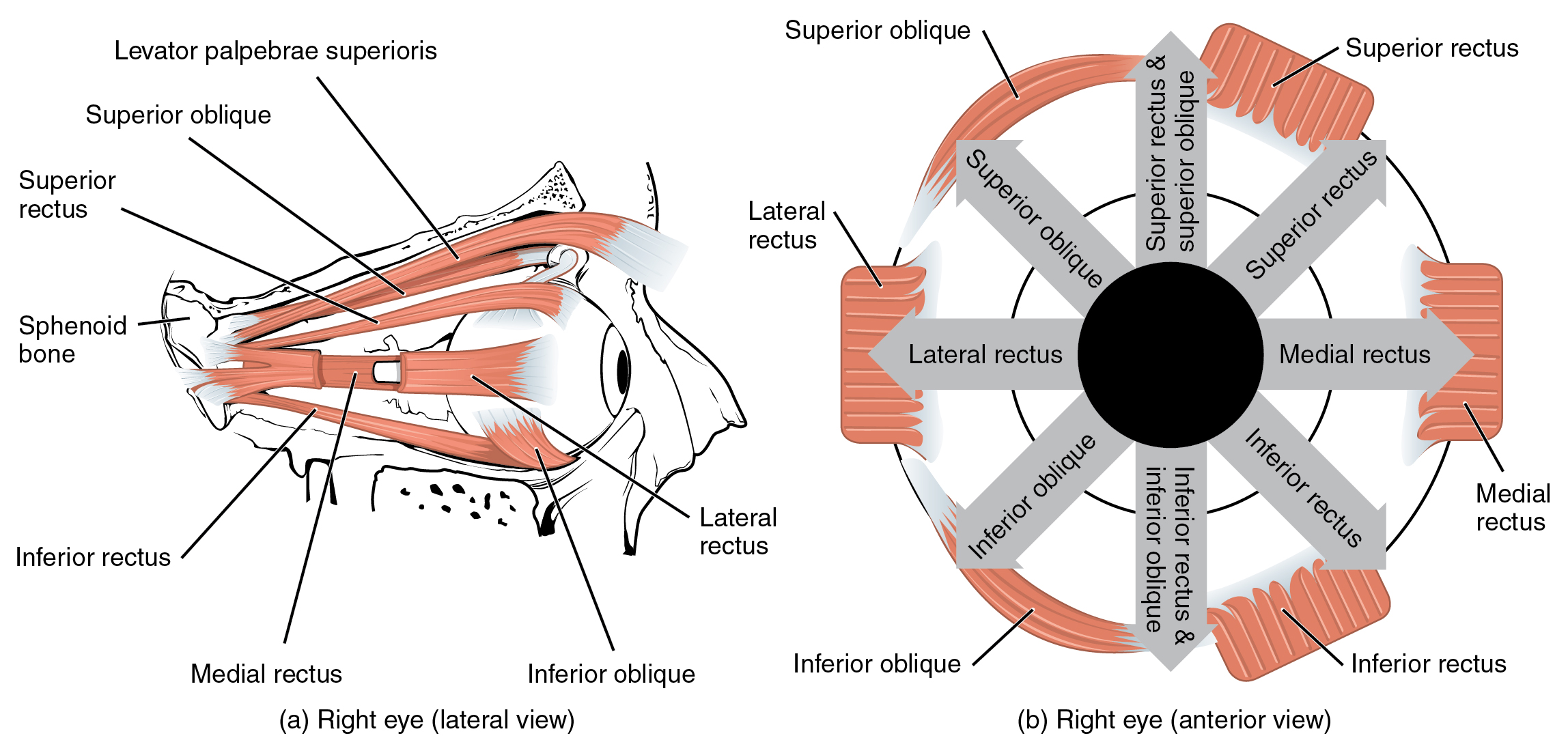
| Muscles of the Eyes (Table 11.3) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Prime mover | Origin | Insertion |
| Moves eyes up and toward nose; rotates eyes from 1 o’clock to 3 o’clock | Eyeballs | Superior (elevates); medial (adducts) | Superior rectus | Common tendinous ring (ring attaches to optic foramen) | Superior surface of eyeball |
| Moves eyes down and toward nose; rotates eyes from 6 o’clock to 3 o’clock | Eyeballs | Inferior (depresses); medial (adducts) | Inferior rectus | Common tendinous ring (ring attaches to optic foramen) | Inferior surface of eyeball |
| Moves eyes away from nose | Eyeballs | Lateral (abducts) | Lateral rectus | Common tendinous ring (ring attaches to optic foramen) | Lateral surface of eyeball |
| Moves eyes toward nose | Eyeballs | Medial (adducts) | Medial rectus | Common tendinous ring (ring attaches to optic foramen) | Medial surface of eyeball |
| Moves eyes up and away from nose; rotates eyeball from 12 o’clock to 9 o’clock | Eyeballs | Superior (elevates); lateral (abducts) | Inferior oblique | Floor of orbit (maxilla) | Surface of eyeball between inferior rectus and lateral rectus |
| Moves eyes down and away from nose; rotates eyeball from 6 o’clock to 9 o’clock | Eyeballs | Superior (elevates); lateral (abducts) | Superior oblique | Sphenoid bone | Suface of eyeball between superior rectus and lateral rectus |
| Opens eyes | Upper eyelid | Superior (elevates) | Levator palpabrae superioris | Roof of orbit (sphenoid bone) | Skin of upper eyelids |
| Closes eyelids | Eyelid skin | Compression along superior–inferior axis | Orbicularis oculi | Medial bones composing the orbit | Circumference of orbit |
Muscles of the Eyes
| Prime mover | Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Origin | Insertion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Superior rectus | Moves eyes up and toward nose; rotates eyes from 1 o’clock to 3 o’clock | Eyeballs | Superior (elevates); medial (adducts) | Common tendinous ring (ring attaches to optic foramen) | Superior surface of eyeball |
| Inferior rectus | Moves eyes down and toward nose; rotates eyes from 6 o’clock to 3 o’clock | Eyeballs | Inferior (depresses); medial (adducts) | Common tendinous ring (ring attaches to optic foramen) | Inferior surface of eyeball |
| Lateral rectus | Moves eyes away from nose | Eyeballs | Lateral (abducts) | Common tendinous ring (ring attaches to optic foramen) | Lateral surface of eyeball |
| Medial rectus | Moves eyes toward nose | Eyeballs | Medial (adducts) | Common tendinous ring (ring attaches to optic foramen) | Medial surface of eyeball |
| Inferior oblique | Moves eyes up and away from nose; rotates eyeball from 12 o’clock to 9 o’clock | Eyeballs | Superior (elevates); lateral (abducts) | Floor of orbit (maxilla) | Surface of eyeball between inferior rectus and lateral rectus |
| Superior oblique | Moves eyes down and away from nose; rotates eyeball from 6 o’clock to 9 o’clock | Eyeballs | Superior (elevates); lateral (abducts) | Sphenoid bone | Suface of eyeball between superior rectus and lateral rectus |
| Levator palpabrae superioris | Opens eyes | Upper eyelid | Superior (elevates) | Roof of orbit (sphenoid bone) | Skin of upper eyelids |
| Orbicularis oculi | Closes eyelids | Eyelid skin | Compression along superior–inferior axis | Medial bones composing the orbit | Circumference of orbit |
Muscles That Move the Lower Jaw
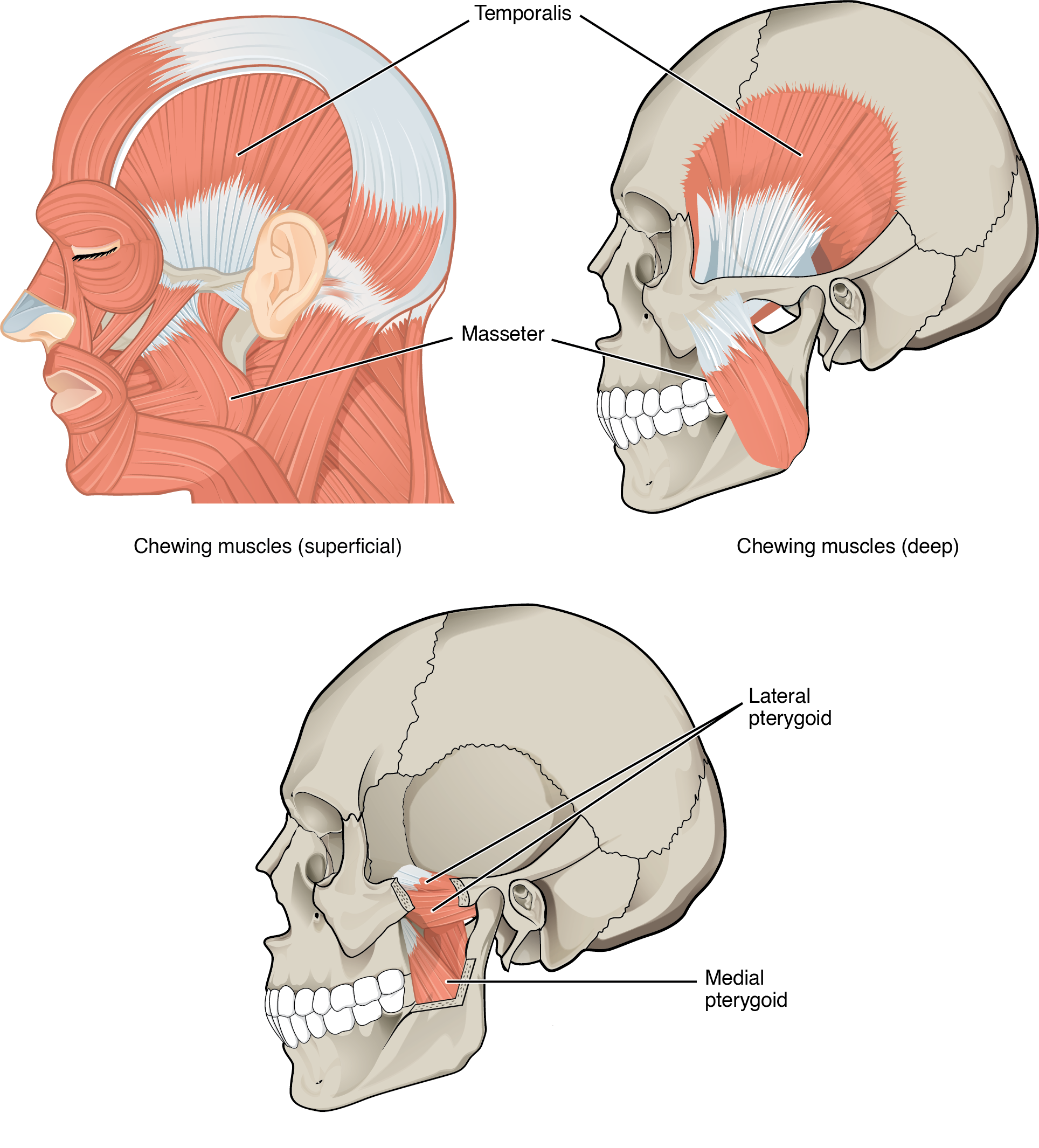
In anatomical terminology, chewing is called mastication. Muscles involved in chewing must be able to exert enough pressure to bite through and then chew food before it is swallowed (Figure 11.4.4 and Table 11.4). The masseter muscle is the prime mover muscle for chewing because it elevates the mandible (lower jaw) to close the mouth, and it is assisted by the temporalis muscle, which retracts the mandible. You can feel the temporalis move by putting your fingers to your temple as you chew. The medial pterygoid and lateral pterygoid muscles provide assistance in chewing and moving food within the mouth by moving the mandible laterally and medially to grind food between the molars.
| Muscles of the Lower Jaw (Table 11.4) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Prime mover | Origin | Insertion |
| Closes mouth; aids chewing | Mandible | Superior (elevates) | Masseter | Maxilla arch; zygomatic arch (for masseter) | Mandible |
| Closes mouth; pulls lower jaw in under upper jaw | Mandible | Superior (elevates); posterior (retracts) | Temporalis | Temporal bone | Mandible |
| Opens mouth; pushes lower jaw out under upper jaw; moves lower jaw side-to-side | Mandible | Inferior (depresses); posterior (protracts); lateral (abducts); medial (adducts) | Lateral pterygoid | Pterygoid process of sphenoid bone | Mandible |
| Closes mouth; pushes lower jaw out under upper jaw; moves lower jaw side-to-side | Mandible | Superior (elevates); posterior (protracts); lateral (abducts); medial (adducts) | Medial pterygoid | Sphenoid bone; maxilla | Mandible; temporo-mandibular joint |
Muscles of the Lower Jaw
| Prime mover | Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Origin | Insertion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masseter | Closes mouth; aids chewing | Mandible | Superior (elevates) | Maxilla arch; zygomatic arch (for masseter) | Mandible |
| Temporalis | Closes mouth; pulls lower jaw in under upper jaw | Mandible | Superior (elevates); posterior (retracts) | Temporal bone | Mandible |
| Lateral pterygoid | Opens mouth; pushes lower jaw out under upper jaw; moves lower jaw side-to-side | Mandible | Lateral (abducts) | Pterygoid process of sphenoid bone | Mandible |
| Medial pterygoid | Closes mouth; pushes lower jaw out under upper jaw; moves lower jaw side-to-side | Mandible | Medial (adducts) | Sphenoid bone; maxilla | Mandible; temporo-mandibular joint |
Muscles That Move the Tongue
Although the tongue is obviously important for tasting food, it is also necessary for mastication, deglutition (swallowing), and speech (Figure 11.4.5 and Figure 11.4.6). Because of its mobility, the tongue facilitates complex speech patterns and sounds.
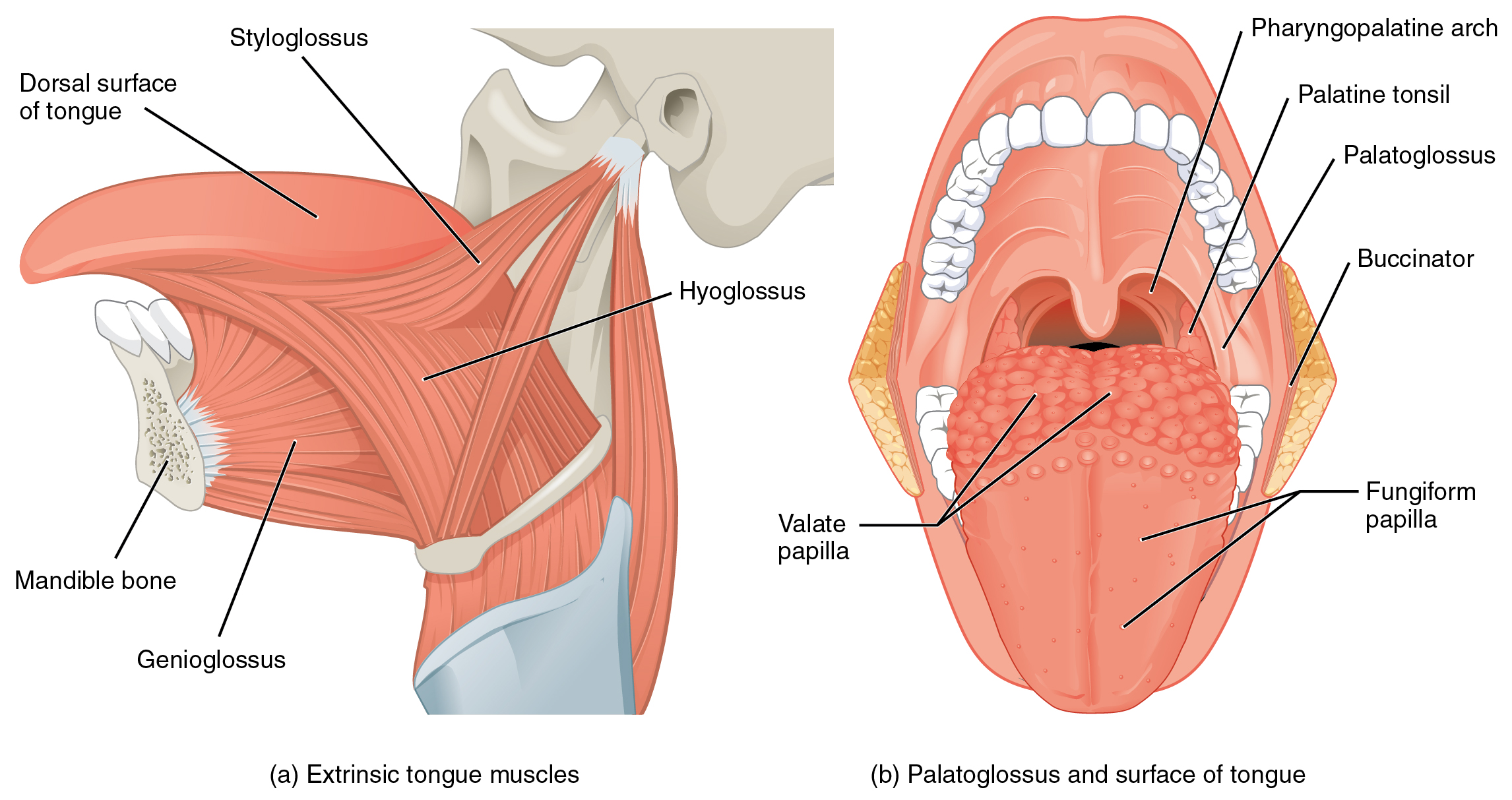
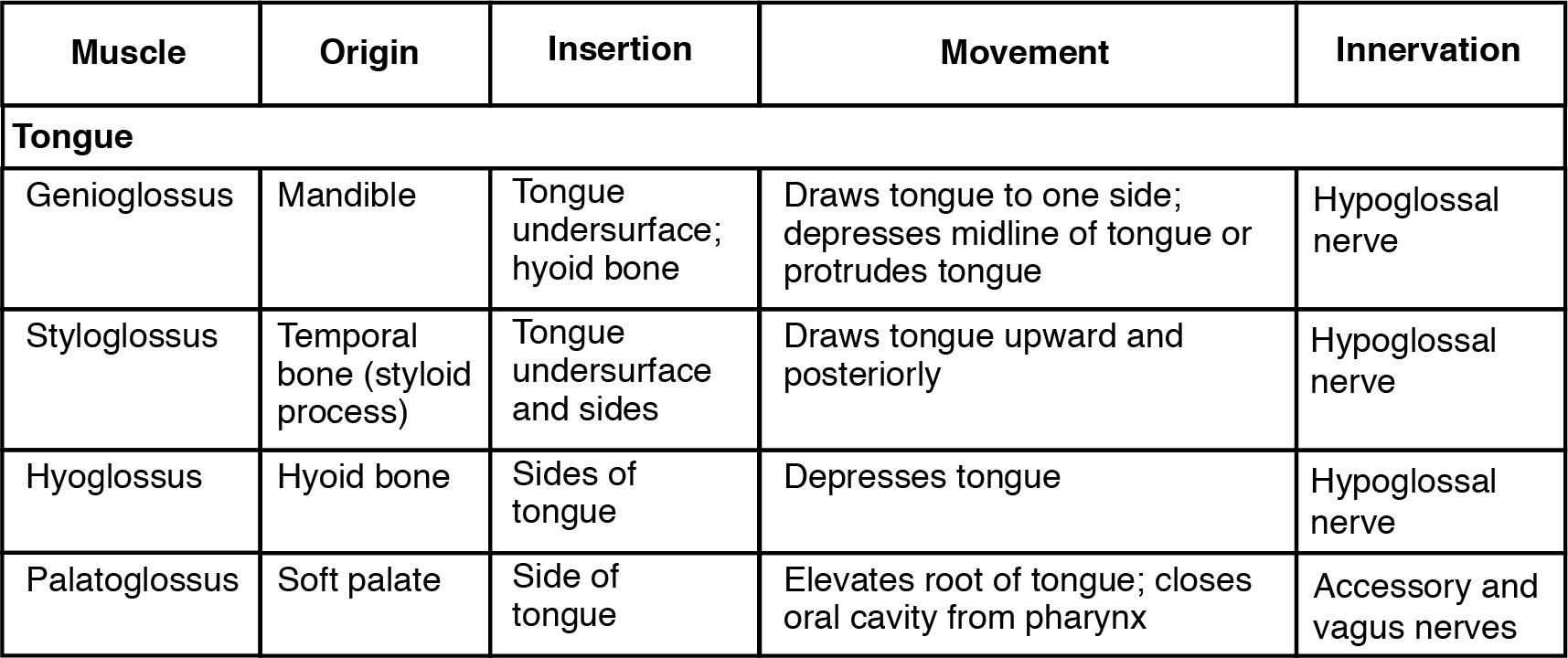
Muscles for Tongue Movement, Swallowing, and Speech
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Movement | Innervation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tongue | ||||
| Genioglossus | Mandible | Tongue undersurface; hyoid bone | Draws tongue to one side; depresses midline of tongue or protrudes tongue | Hypoglossal nerve |
| Styloglossus | Temporal bone (styloid process) | Tongue undersurface and sides | Draws tongue upward and posteriorly | Hypoglossal nerve |
| Hyoglossus | Temporal bone (styloid bone) | Sides of tongue | Depresses tongue | Hypoglossal nerve |
| Palatoglossus | Soft palate | Side of tongue | Elevates root of tongue; closes oral cavity from pharynx | Accessory and vagus nerves |
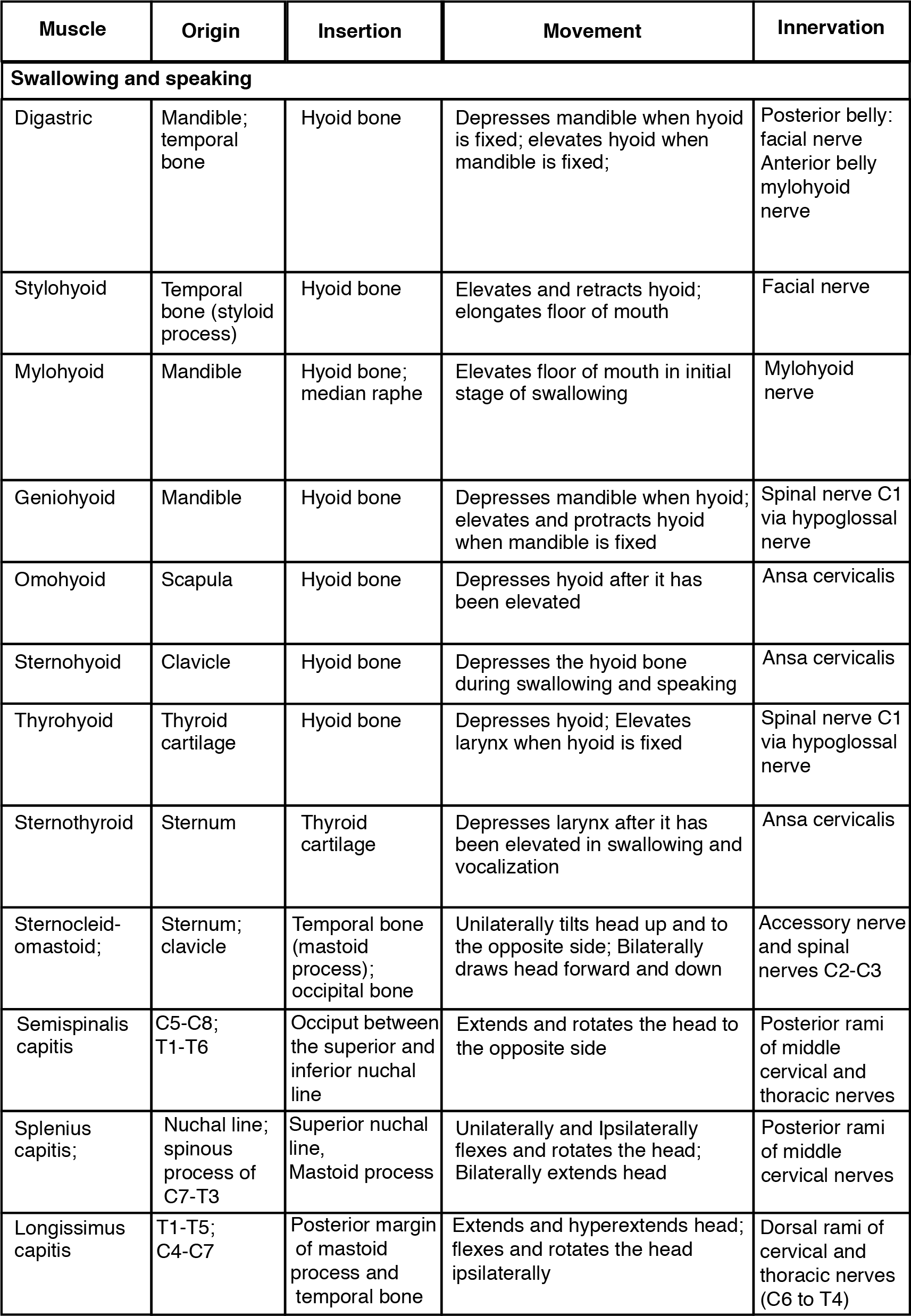
Muscles for Tongue Movement, Swallowing, and Speech
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Movement | Innervation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swallowing and speaking | ||||
| Digastric | Mandible; temporal bone | Hyoid bone | Depresses mandible when hyoid is fixed; elevates hyoid when mandible is fixed; | Posterior belly; facial nerve Anterior belly mylohyoid nerve |
| Stylohyoid | Temporal bone (styloid process) | Hyoid bone | Elevates and retracts hyoid; elongates floor of mouth | Facial nerve |
| Mylohyoid | Mandible | Hyoid bone; median raphe | Elevates floor of mouth in initial stage of swallowing | Mylohyoid nerve |
| Geniohyoid | Mandible | Hyoid bone | Depresses mandible when hyoid; elevates and protracts hyoid when mandible is fixed | Spinal nerve C1 via hypoglossal nerve |
| Omohyoid | Scapula | Hyoid bone | Depresses hyoid after it has been elevated | Ansa cervicalis |
| Sternohyoid | Clavicle | Hyoid bone | Depresses the hyoid during swallowing and speaking | Ansa cervicalis |
| Thyrohyoid | Thyroid cartilage | Hyoid bone | Depresses hyoid; Elevates larynx when hyoid is fixed | Spinal nerve C1 via hypoglossal nerve |
| Sternothyroid | Sternum | Thyroid cartilage | Depresses larynx after it has been elevated in swallowing and vocalization | Ansa cervicalis |
| Sternocleid- omastoid; | Sternum; clavicle | Temporal bone (mastoid process); occipital bone | Unilaterally tilts head up and to the opposite side; Bilaterally draws head forward and down | Accessory nerve and spinal nerves C2-C3 |
| Semispinalis capitis | C5-C8; T1-T6 | Occiput between the superior and inferior nuchal line | Extends and rotates the head to the opposite side | Posterior rami of middle cervical and thoracic nerves |
| Splenius capitis; | Nuchal line; spinous process of C7-T3 | Superior nuchal line, Mastoid process | Unilaterally and ipsilaterally flexes and rotates the head; Bilaterally extends head | Posterior rami of middle cervical nerves |
| Longissimus capitis | T1-T5; C4-C7 | Posterior margin of mastoid process and temporal bone | Extends and hyperextends head; flexes and rotates the head ipsilaterally | Dorsal rami of cervical and thoracic nerves (C6 to T4) |
Tongue muscles can be extrinsic or intrinsic. Extrinsic tongue muscles insert into the tongue from outside origins, and the intrinsic tongue muscles insert into the tongue from origins within it. The extrinsic muscles move the whole tongue in different directions, whereas the intrinsic muscles allow the tongue to change its shape (such as, curling the tongue in a loop or flattening it).
The extrinsic muscles all include the word root glossus (glossus = “tongue”), and the muscle names are derived from where the muscle originates. The genioglossus (genio = “chin”) originates on the mandible and allows the tongue to move downward and forward. The styloglossus originates on the styloid process of the temporal bone, and allows upward and backward motion. The palatoglossus originates on the soft palate to elevate the back of the tongue, and the hyoglossus originates on the hyoid bone to move the tongue downward and flatten it.
Muscles of the Anterior Neck
The muscles of the anterior neck assist in deglutition (swallowing) and speech by controlling the positions of the larynx (voice box), and the hyoid bone, a horseshoe-shaped bone that functions as a foundation on which the tongue can move. The muscles of the neck are categorized according to their position relative to the hyoid bone (Figure 11.4.7). Suprahyoid muscles are superior to it, and the infrahyoid muscles are located inferiorly.
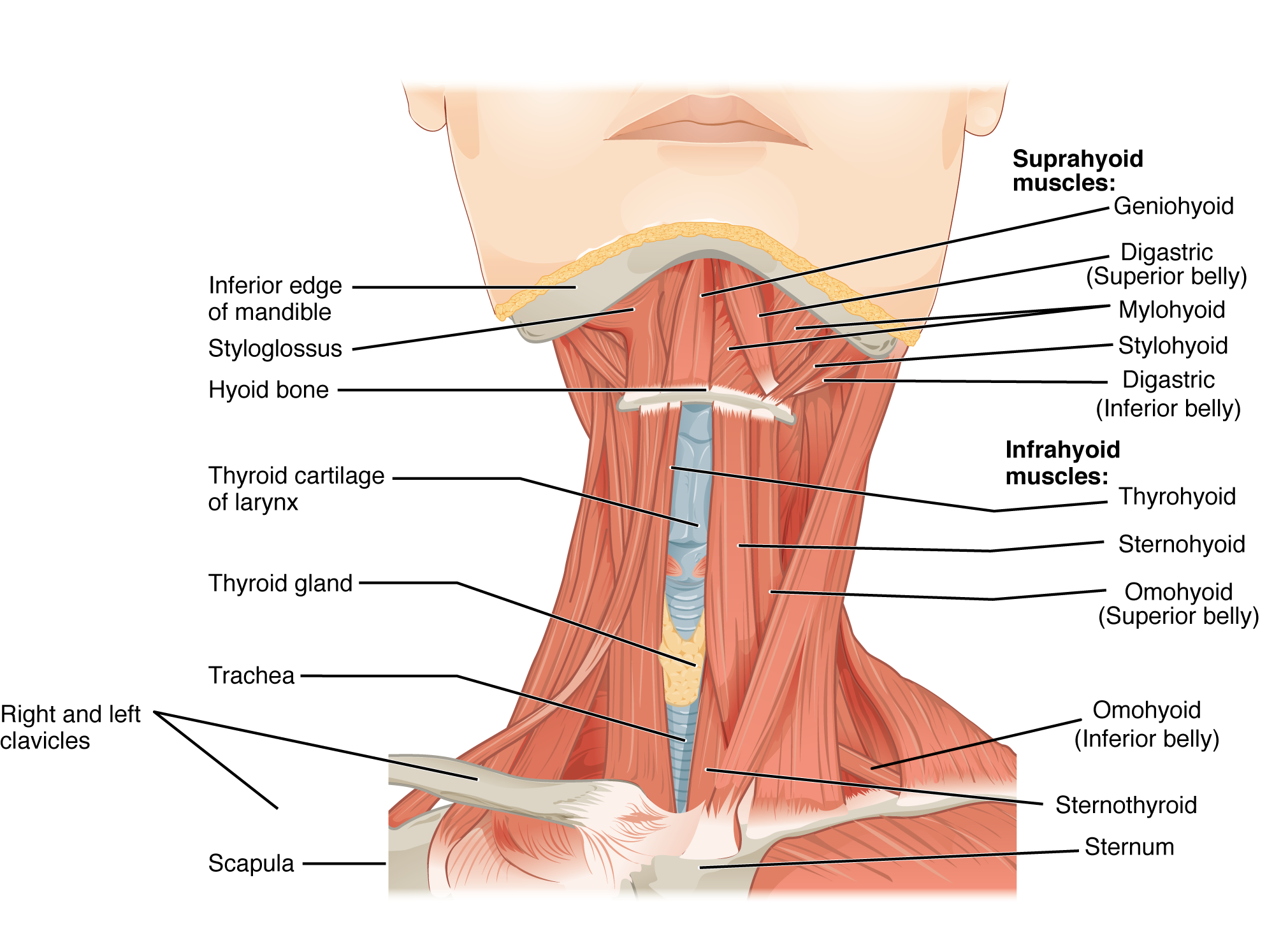
The suprahyoid muscles raise the hyoid bone, the floor of the mouth, and the larynx during deglutition. These include the digastric muscle, which has anterior and posterior bellies that work to elevate the hyoid bone and larynx when one swallows; it also depresses the mandible. The stylohyoid muscle moves the hyoid bone posteriorly, elevating the larynx, and the mylohyoid muscle lifts it and helps press the tongue to the top of the mouth. The geniohyoid depresses the mandible in addition to raising and pulling the hyoid bone anteriorly.
The strap-like infrahyoid muscles generally depress the hyoid bone and control the position of the larynx. The omohyoid muscle, which has superior and inferior bellies, depresses the hyoid bone in conjunction with the sternohyoid and thyrohyoid muscles. The thyrohyoid muscle also elevates the larynx’s thyroid cartilage, whereas the sternothyroid depresses it.
Muscles That Move the Head
The head is balanced, moved and rotated by the neck muscles (Table 11.5). When these muscles act unilaterally, the head rotates. When they contract bilaterally, the head flexes or extends. The major muscle that laterally flexes and rotates the head is the sternocleidomastoid. In addition, both muscles working together are the flexors of the head. Place your fingers on both sides of the neck and turn your head to the left and to the right. You will feel the movement originate there. This muscle divides the neck into anterior and posterior triangles when viewed from the side (Figure 11.4.8).
| Muscles That Move the Head (Table 11.5) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Prime mover | Origin | Insertion |
| Rotates and tilts head to the side; tilts head forward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: rotates head to opposite side; bilaterally: flexion | Sternocleidomastoid | Sternum; clavicle | Temporal bone (mastoid process); occipital bone |
| Rotates and tilts head backward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: laterally flexes and rotates head to same side; bilaterally: extension | Semispinalis capitis | Transverse and articular processes of cervical and thoracic vertebra | Occipital bone |
| Rotates and tilts head to the side; tilts head backward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: laterally flexes and rotates head to same side; bilaterally: extension | Splenius capitis | Spinous processes of cervical and thoracic vertebra | Temporal bone (mastoid process); occipital bone |
| Rotates and tilts head to the side; tilts head backward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: laterally flexes and rotates head to same side; bilaterally: extension | Longissimus capitis | Transverse and articular processes of cervical and thoracic vertebra | Temporal bone (mastoid process) |
Muscles That Move the Head
| Prime mover | Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Origin | Insertion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sternocleidomastoid | Rotates and tilts head to the side; tilts head forward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: rotates head to opposite side; bilaterally: flexion | Sternum; clavicle | Temporal bone (mastoid process); occipital bone |
| Semispinalis capitis | Rotates and tilts head backward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: laterally flexes and rotates head to same side; bilaterally: extension | Transverse and articular processes of cervical and thoracic vertebra | Occipital bone |
| Splenius capitis | Rotates and tilts head to the side; tilts head backward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: laterally flexes and rotates head to same side; bilaterally: extension | Spinous processes of cervical and thoracic vertebra | Temporal bone (mastoid process); occipital bone |
| Longissimus capitis | Rotates and tilts head to the side; tilts head backward | Skull; vertebrae | Individually: laterally flexes and rotates head to same side; bilaterally: extension | Transverse and articular processes of cervical and thoracic vertebra | Temporal bone (mastoid process) |
Muscles of the Posterior Neck and the Back
The posterior muscles of the neck are primarily concerned with head movements, like extension. The back muscles stabilize and move the vertebral column, and are grouped according to the lengths and direction of the fascicles.
The splenius muscles originate at the midline and run laterally and superiorly to their insertions. From the sides and the back of the neck, the splenius capitis inserts onto the head region, and the splenius cervicis extends onto the cervical region. These muscles can extend the head, laterally flex it, and rotate it (Figure 11.4.8).
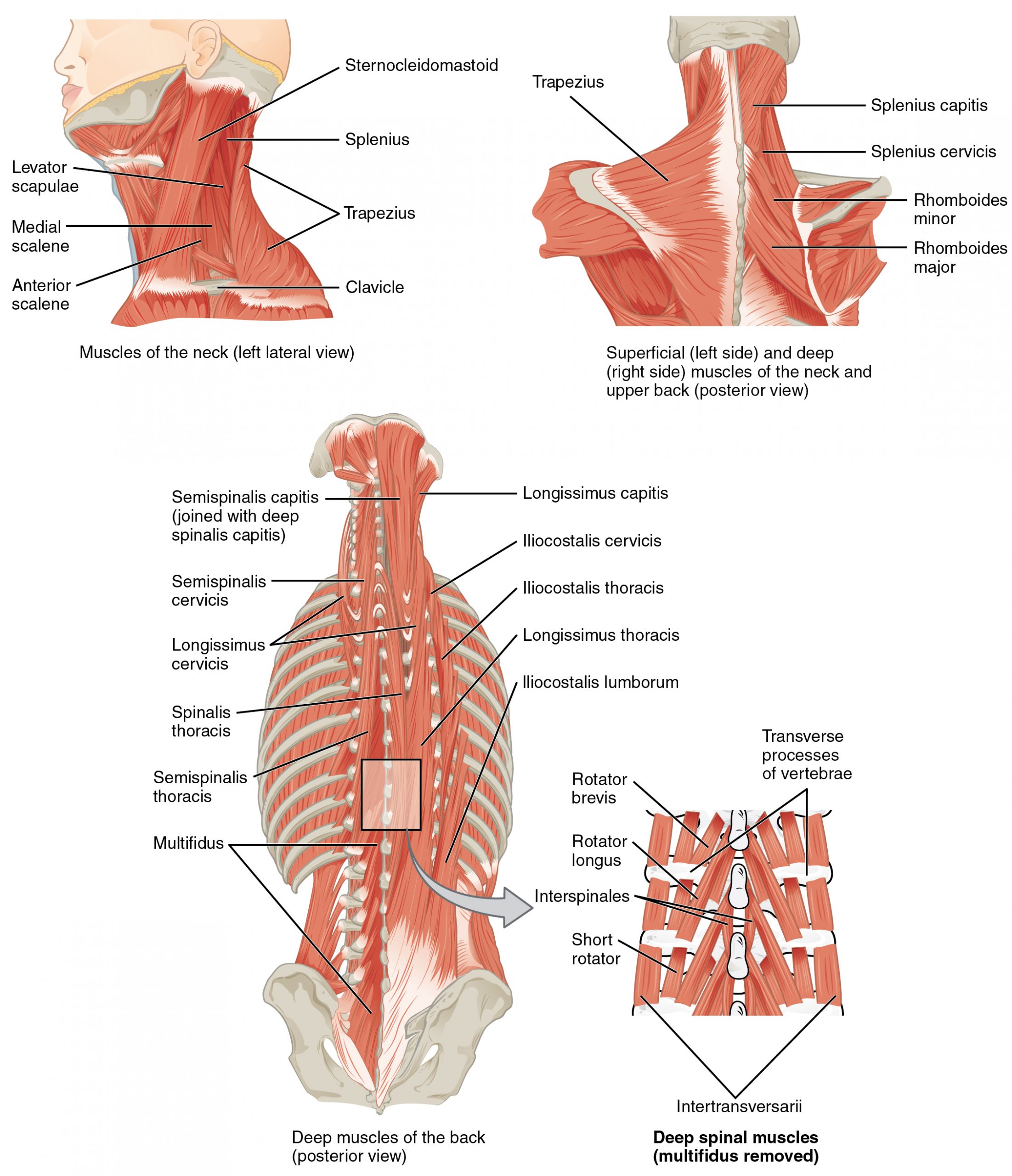
The erector spinae group forms the majority of the muscle mass of the back and it is the primary extensor of the vertebral column. It controls extension, lateral flexion, and rotation of the vertebral column, and maintains the lumbar curve. The erector spinae comprises the iliocostalis (laterally placed) group, the longissimus (intermediately placed) group, and the spinalis (medially placed) group.
The iliocostalis group includes the iliocostalis cervicis, associated with the cervical region; the iliocostalis thoracis, associated with the thoracic region; and the iliocostalis lumborum, associated with the lumbar region. The three muscles of the longissimus group are the longissimus capitis, associated with the head region; the longissimus cervicis, associated with the cervical region; and the longissimus thoracis, associated with the thoracic region. The third group, the spinalis group, comprises the spinalis capitis (head region), the spinalis cervicis (cervical region), and the spinalis thoracis (thoracic region).
The transversospinales muscles run from the transverse processes to the spinous processes of the vertebrae. Similar to the erector spinae muscles, the semispinalis muscles in this group are named for the areas of the body with which they are associated. The semispinalis muscles include the semispinalis capitis, the semispinalis cervicis, and the semispinalis thoracis. The multifidus muscle of the lumbar region helps extend and laterally flex the vertebral column.
Important in the stabilization of the vertebral column is the segmental muscle group, which includes the interspinales and intertransversarii muscles. These muscles bring together the spinous and transverse processes of each consecutive vertebra. Finally, the scalene muscles work together to flex, laterally flex, and rotate the head. They also contribute to deep inhalation. The scalene muscles include the anterior scalene muscle (anterior to the middle scalene), the middle scalene muscle (the longest, intermediate between the anterior and posterior scalenes), and the posterior scalene muscle (the smallest, posterior to the middle scalene).
Chapter Review
Muscles are either axial muscles or appendicular. The axial muscles are grouped based on location, function, or both. Some axial muscles cross over to the appendicular skeleton. The muscles of the head and neck are all axial. The muscles in the face create facial expression by inserting into the skin rather than onto bone. Muscles that move the eyeballs are extrinsic, meaning they originate outside of the eye and insert onto it. Tongue muscles are both extrinsic and intrinsic. The genioglossus depresses the tongue and moves it anteriorly; the styloglossus lifts the tongue and retracts it; the palatoglossus elevates the back of the tongue; and the hyoglossus depresses and flattens it. The muscles of the anterior neck facilitate swallowing and speech, stabilize the hyoid bone and position the larynx. The muscles of the neck stabilize and move the head. The sternocleidomastoid divides the neck into anterior and posterior triangles.
The muscles of the back and neck that move the vertebral column are complex, overlapping, and can be divided into five groups. The splenius group includes the splenius capitis and the splenius cervicis. The erector spinae has three subgroups. The iliocostalis group includes the iliocostalis cervicis, the iliocostalis thoracis, and the iliocostalis lumborum. The longissimus group includes the longissimus capitis, the longissimus cervicis, and the longissimus thoracis. The spinalis group includes the spinalis capitis, the spinalis cervicis, and the spinalis thoracis. The transversospinales include the semispinalis capitis, semispinalis cervicis, semispinalis thoracis, multifidus, and rotatores. The segmental muscles include the interspinales and intertransversarii. Finally, the scalenes include the anterior scalene, middle scalene, and posterior scalene.
Review Questions
Critical Thinking Questions
1. Explain the difference between axial and appendicular muscles.
2. Describe the muscles of the anterior neck.
3. Why are the muscles of the face different from typical skeletal muscle?
Glossary
- anterior scalene
- a muscle anterior to the middle scalene
- appendicular
- of the arms and legs
- axial
- of the trunk and head
- buccinator
- muscle that compresses the cheek
- corrugator supercilii
- prime mover of the eyebrows
- deglutition
- swallowing
- digastric
- muscle that has anterior and posterior bellies and elevates the hyoid bone and larynx when one swallows; it also depresses the mandible
- epicranial aponeurosis
- (also, galea aponeurosis) flat broad tendon that connects the frontalis and occipitalis
- erector spinae group
- large muscle mass of the back; primary extensor of the vertebral column
- extrinsic eye muscles
- originate outside the eye and insert onto the outer surface of the white of the eye, and create eyeball movement
- frontalis
- front part of the occipitofrontalis muscle
- genioglossus
- muscle that originates on the mandible and allows the tongue to move downward and forward
- geniohyoid
- muscle that depresses the mandible, and raises and pulls the hyoid bone anteriorly
- hyoglossus
- muscle that originates on the hyoid bone to move the tongue downward and flatten it
- iliocostalis cervicis
- muscle of the iliocostalis group associated with the cervical region
- iliocostalis group
- laterally placed muscles of the erector spinae
- iliocostalis lumborum
- muscle of the iliocostalis group associated with the lumbar region
- iliocostalis thoracis
- muscle of the iliocostalis group associated with the thoracic region
- infrahyoid muscles
- anterior neck muscles that are attached to, and inferior to the hyoid bone
- lateral pterygoid
- muscle that moves the mandible from side to side
- longissimus capitis
- muscle of the longissimus group associated with the head region
- longissimus cervicis
- muscle of the longissimus group associated with the cervical region
- longissimus group
- intermediately placed muscles of the erector spinae
- longissimus thoracis
- muscle of the longissimus group associated with the thoracic region
- masseter
- main muscle for chewing that elevates the mandible to close the mouth
- mastication
- chewing
- medial pterygoid
- muscle that moves the mandible from side to side
- middle scalene
- longest scalene muscle, located between the anterior and posterior scalenes
- multifidus
- muscle of the lumbar region that helps extend and laterally flex the vertebral column
- mylohyoid
- muscle that lifts the hyoid bone and helps press the tongue to the top of the mouth
- occipitalis
- posterior part of the occipitofrontalis muscle
- occipitofrontalis
- muscle that makes up the scalp with a frontal belly and an occipital belly
- omohyoid
- muscle that has superior and inferior bellies and depresses the hyoid bone
- orbicularis oculi
- circular muscle that closes the eye
- orbicularis oris
- circular muscle that moves the lips
- palatoglossus
- muscle that originates on the soft palate to elevate the back of the tongue
- posterior scalene
- smallest scalene muscle, located posterior to the middle scalene
- scalene muscles
- flex, laterally flex, and rotate the head; contribute to deep inhalation
- segmental muscle group
- interspinales and intertransversarii muscles that bring together the spinous and transverse processes of each consecutive vertebra
- semispinalis capitis
- transversospinales muscle associated with the head region
- semispinalis cervicis
- transversospinales muscle associated with the cervical region
- semispinalis thoracis
- transversospinales muscle associated with the thoracic region
- spinalis capitis
- muscle of the spinalis group associated with the head region
- spinalis cervicis
- muscle of the spinalis group associated with the cervical region
- spinalis group
- medially placed muscles of the erector spinae
- spinalis thoracis
- muscle of the spinalis group associated with the thoracic region
- splenius
- posterior neck muscles; includes the splenius capitis and splenius cervicis
- splenius capitis
- neck muscle that inserts into the head region
- splenius cervicis
- neck muscle that inserts into the cervical region
- sternocleidomastoid
- major muscle that laterally flexes and rotates the head
- sternohyoid
- muscle that depresses the hyoid bone
- sternothyroid
- muscle that depresses the larynx’s thyroid cartilage
- styloglossus
- muscle that originates on the styloid bone, and allows upward and backward motion of the tongue
- stylohyoid
- muscle that elevates the hyoid bone posteriorly
- suprahyoid muscles
- neck muscles that are superior to the hyoid bone
- temporalis
- muscle that retracts the mandible
- thyrohyoid
- muscle that depresses the hyoid bone and elevates the larynx’s thyroid cartilage
- transversospinales
- muscles that originate at the transverse processes and insert at the spinous processes of the vertebrae
- trapezius
- muscle that stabilizes the upper part of the back
Solutions
Answers for Critical Thinking Questions
- Axial muscles originate on the axial skeleton (the bones in the head, neck, and core of the body), whereas appendicular muscles originate on the bones that make up the body’s limbs.
- The muscles of the anterior neck are arranged to facilitate swallowing and speech. They work on the hyoid bone, with the suprahyoid muscles pulling up and the infrahyoid muscles pulling down.
- Most skeletal muscles create movement by actions on the skeleton. Facial muscles are different in that they create facial movements and expressions by pulling on the skin—no bone movements are involved.
This work, Anatomy & Physiology, is adapted from Anatomy & Physiology by OpenStax, licensed under CC BY. This edition, with revised content and artwork, is licensed under CC BY-SA except where otherwise noted.
Images, from Anatomy & Physiology by OpenStax, are licensed under CC BY except where otherwise noted.
Access the original for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction.

