Chapter 10: Antimicrobial Drugs
Chapter Outline
10.1 Fundamentals of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
10.2 Mechanisms of Antibacterial Drugs
10.3 Mechanisms of Other Antimicrobial Drugs
14.4 Drug Resistance
10.5 Testing the Effectiveness of Antimicrobials
10.6 Current Strategies for Antimicrobial Discovery
Introduction
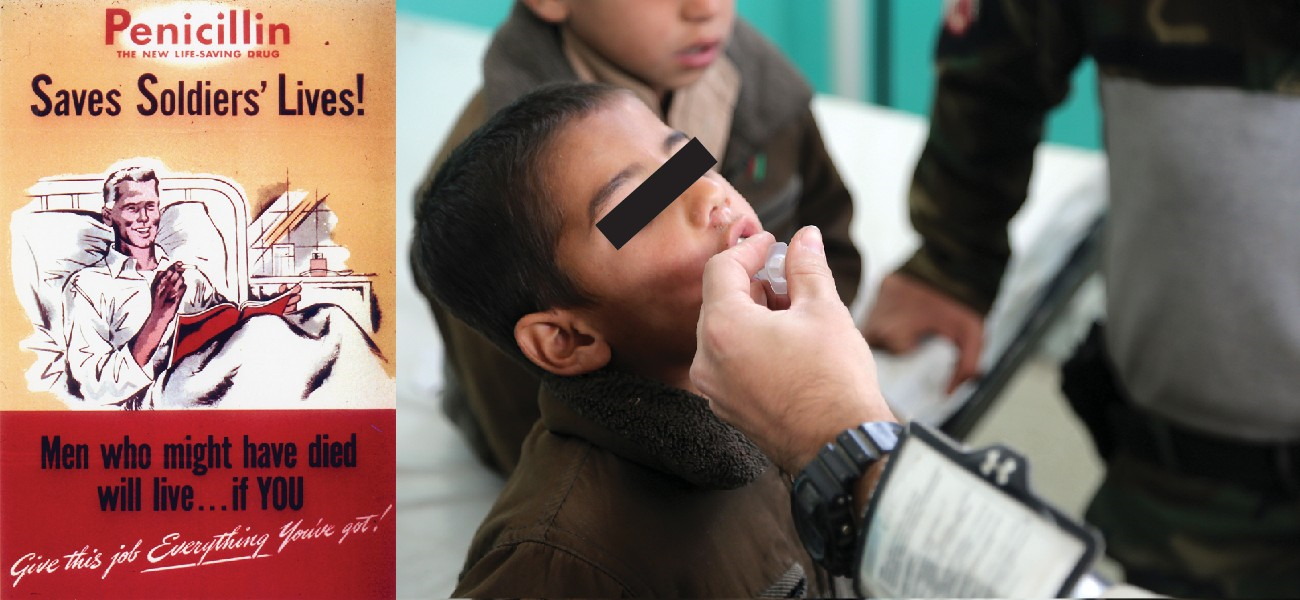
In nature, some microbes produce substances that inhibit or kill other microbes that might otherwise compete for the same resources. Humans have successfully exploited these abilities, using microbes to mass-produce substances that can be used as antimicrobial drugs (see Figure 10.1). Since their discovery, antimicrobial drugs have saved countless lives, and they remain an essential tool for treating and controlling infectious disease. But their widespread and often unnecessary use has had an unintended side effect: the rise of multidrug-resistant microbial strains. In this chapter, we will discuss how antimicrobial drugs work, why microbes develop resistance, and what health professionals can do to encourage responsible use of antimicrobials.

