20.1 Anatomy of the Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems
Learning Objectives
- Describe the major anatomical features of the circulatory and lymphatic systems
- Explain why the circulatory and lymphatic systems lack normal microbiota
- Explain how microorganisms overcome defenses of the circulatory and lymphatic systems to cause infection
- Describe general signs and symptoms of disease associated with infections of the circulatory and lymphatic systems
The circulatory and lymphatic systems are networks of vessels and a pump that transport blood and lymph, respectively, throughout the body. When these systems are infected with a microorganism, the network of vessels can facilitate the rapid dissemination of the microorganism to other regions of the body, sometimes with serious results. In this section, we will examine some of the key anatomical features of the circulatory and lymphatic systems, as well as general signs and symptoms of infection.
The Circulatory System
The circulatory (or cardiovascular) system is a closed network of organs and vessels that moves blood around the body (Figure 20.2). The primary purposes of the circulatory system are to deliver nutrients, immune factors, and oxygen to tissues and to carry away waste products for elimination. The heart is a four-chambered pump that propels the blood throughout the body. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava after returning from the body. The blood next passes through the tricuspid valve to enter the right ventricle. When the heart contracts, the blood from the right ventricle is pumped through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs. There, the blood is oxygenated at the alveoli and returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins. The oxygenated blood is received at the left atrium and proceeds through the mitral valve to the left ventricle. When the heart contracts, the oxygenated blood is pumped throughout the body via a series of thick-walled vessels called arteries. The first and largest artery is called the aorta. The arteries sequentially branch and decrease in size (and are called arterioles) until they end in a network of smaller vessels called capillaries. The capillary beds are located in the interstitial spaces within tissues and release nutrients, immune factors, and oxygen to those tissues. The capillaries connect to a series of vessels called venules, which increase in size to form the veins. The veins join together into larger vessels as they transfer blood back to the heart. The largest veins, the superior and inferior vena cava, returnthe blood to the right atrium.
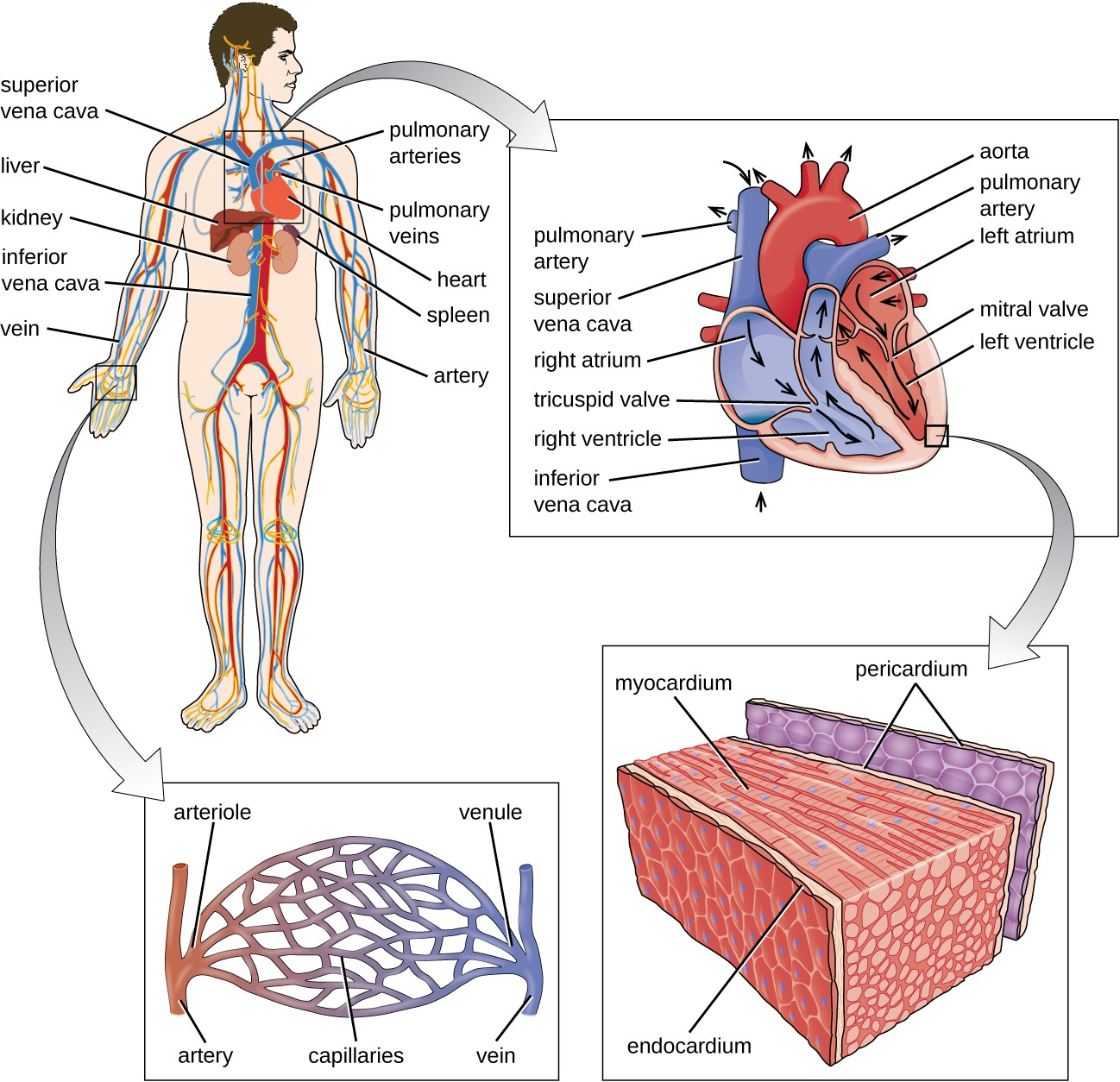
Other organs play important roles in the circulatory system as well. The kidneys filter the blood, removing waste products and eliminating them in the urine. The liver also filters the blood and removes damaged or defective red blood cells. The spleen filters and stores blood, removes damaged red blood cells, and is a reservoir for immune factors. All of these filtering structures serve as sites for entrapment of microorganisms and help maintain an environment free of microorganisms in the blood.
The Lymphatic System
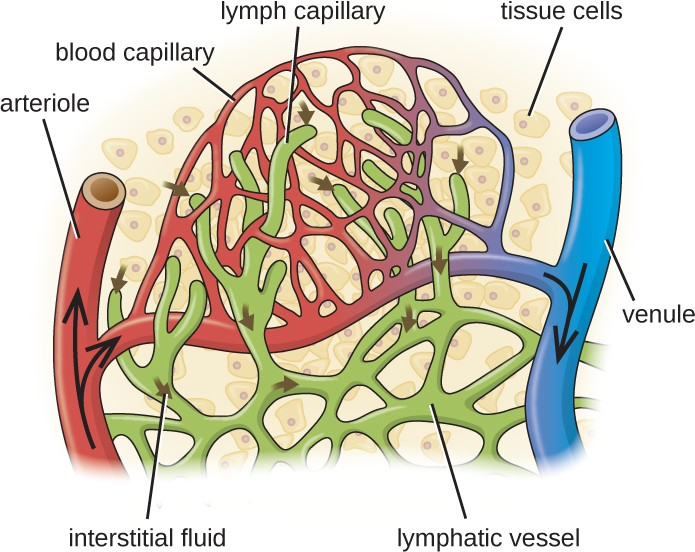
The lymphatic system is also a network of vessels that run throughout the body (Figure 20.3). However, these vessels do not form a full circulating system and are not pressurized by the heart. Rather, the lymphatic system is an open system with the fluid moving in one direction from the extremities toward two drainage points into veins just above the heart. Lymphatic fluids move more slowly than blood because they are not pressurized. Small lymph capillaries interact with blood capillaries in the interstitial spaces in tissues. Fluids from the tissues enter the lymph capillaries and are drained away (Figure 20.4). These fluids, termed lymph, also contain large numbers of white blood cells.
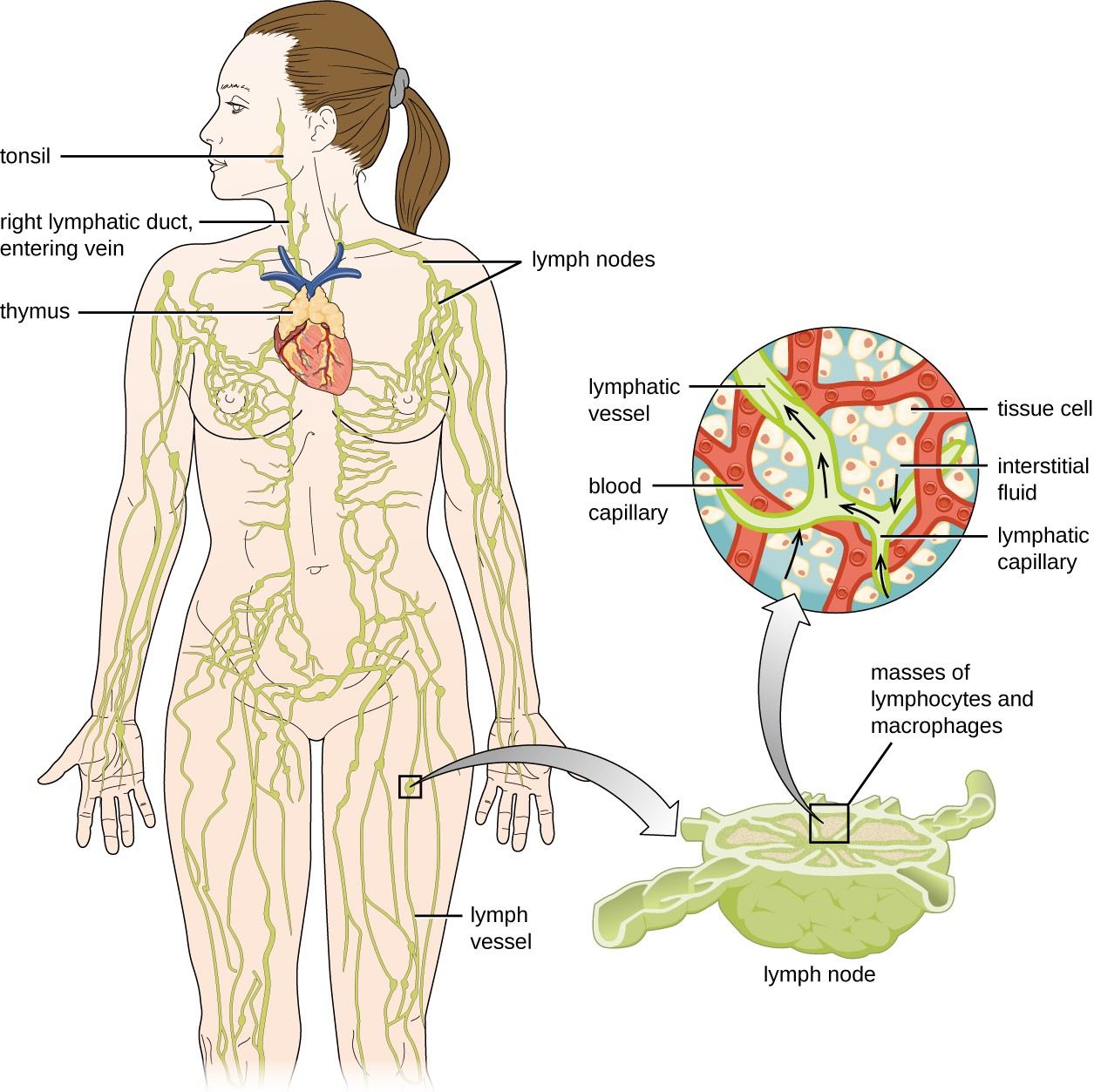
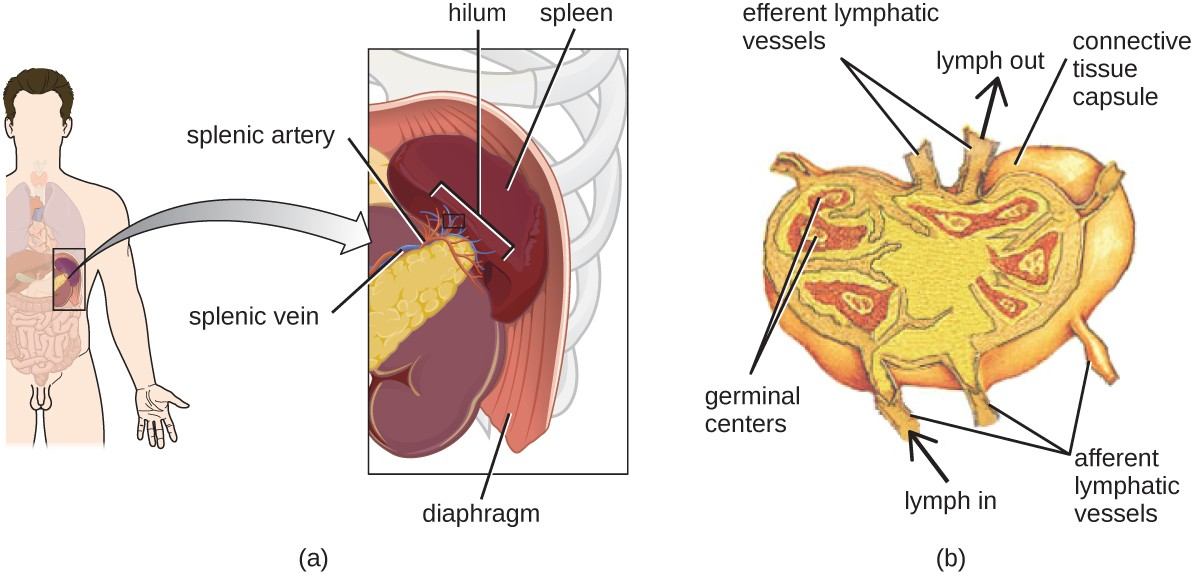
The lymphatic system contains two types of lymphoid tissues. The primary lymphoid tissue includes bone marrow and the thymus. Bone marrow contains the hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) that differentiate and mature into the various types of blood cells and lymphocytes. The secondary lymphoid tissues include the spleen, lymph nodes, and several areas of diffuse lymphoid tissues underlying epithelial membranes. The spleen, an encapsulated structure, filters blood and captures pathogens and antigens that pass into it (Figure 20.5). The spleen contains specialized macrophages and dendritic cells that are crucial for antigen presentation, a mechanism critical for activation of T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes. Lymph nodes are bean-shaped organs situated throughout the body. These structures contain areas called germinal centers that are rich in B and T lymphocytes. The lymph nodes also contain macrophages and dendritic cells for antigen presentation. Lymph from nearby tissues enters the lymph node through afferent lymphatic vessels and encounters these lymphocytes as it passes through; the lymph exits the lymph node through the efferent lymphatic vessels (Figure 20.5).
Link to Learning
The lymphatic system filters fluids that have accumulated in tissues before they are returned to the blood. A brief overview of this process is provided at this website (https://openstax.org/l/22lymphatic).
![]()
- What is the main function of the lymphatic system?
Infections of the Circulatory System
Under normal circumstances, the circulatory system and the blood should be sterile; the circulatory system has no normal microbiota. Because the system is closed, there are no easy portals of entry into the circulatory system for microbes. Those that are able to breach the body’s physical barriers and enter the bloodstream encounter a host of circulating immune defenses, such as antibodies, complement proteins, phagocytes, and other immune cells. Microbes often gain access to the circulatory system through a break in the skin (e.g., wounds, needles, intravenous catheters, insect bites) or spread to the circulatory system from infections in other body sites. For example, microorganisms causing pneumonia or renal infection may enter the local circulation of the lung or kidney and spread from there throughout the circulatory network.
If microbes in the bloodstream are not quickly eliminated, they can spread rapidly throughout the body, leading to serious, even life-threatening infections. Various terms are used to describe conditions involving microbes in the circulatory system. The term bacteremia refers to bacteria in the blood. If bacteria are reproducing in the blood as they spread, this condition is called septicemia. The presence of viruses in the blood is called viremia. Microbial toxins can also be spread through the circulatory system, causing a condition termed toxemia.
Microbes and microbial toxins in the blood can trigger an inflammatory response so severe that the inflammation damages host tissues and organs more than the infection itself. This counterproductive immune response is called systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), and it can lead to the life-threatening condition known as sepsis. Sepsis is characterized by the production of excess cytokines that leads to classic signs of inflammation such as fever, vasodilation, and edema. In a patient with sepsis, the inflammatory response becomes dysregulated and disproportionate to the threat of infection. Critical organs such as the heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys become dysfunctional, resulting in increased heart and respiratory rates, and disorientation. If not treated promptly and effectively, patients with sepsis can go into shock and die.
![]()
- Why does the circulatory system have no normal microbiota?
- Explain why the presence of microbes in the circulatory system can lead to serious consequences.
Infections of the Lymphatic System
Like the circulatory system, the lymphatic system does not have a normal microbiota, and the large numbers of immune cells typically eliminate transient microbes before they can establish an infection. Only microbes with an array of virulence factors are able to overcome these defenses and establish infection in the lymphatic system. However, when a localized infection begins to spread, the lymphatic system is often the first place the invading microbes can be detected.
Infections in the lymphatic system also trigger an inflammatory response. Inflammation of lymphatic vessels, called lymphangitis, can produce visible red streaks under the skin. Inflammation in the lymph nodes can cause them to swell. A swollen lymph node is referred to as a bubo, and the condition is referred to as lymphadenitis.

