12.3 Modes of Disease Transmission
Learning Objectives
- Describe the different types of disease reservoirs
- Compare contact, vector, and vehicle modes of transmission
- Identify important disease vectors
- Explain the prevalence of nosocomial infections
Understanding how infectious pathogens spread is critical to preventing infectious disease. Many pathogens require a living host to survive, while others may be able to persist in a dormant state outside of a living host. But having infected one host, all pathogens must also have a mechanism of transfer from one host to another or they will die when their host dies. Pathogens often have elaborate adaptations to exploit host biology, behavior, and ecology to live in and move between hosts. Hosts have evolved defenses against pathogens, but because their rates of evolution are typically slower than their pathogens (because their generation times are longer), hosts are usually at an evolutionary disadvantage. This section will explore where pathogens survive—both inside and outside hosts—and some of the many ways they move from one host to another.
Reservoirs and Carriers
For pathogens to persist over long periods of time they require reservoirs where they normally reside. Reservoirs can be living organisms or nonliving sites. Nonliving reservoirs can include soil and water in the environment. These may naturally harbor the organism because it may grow in that environment. These environments may also become contaminated with pathogens in human feces, pathogens shed by intermediate hosts, or pathogens contained in the remains of intermediate hosts.
Pathogens may have mechanisms of dormancy or resilience that allow them to survive (but typically not to reproduce) for varying periods of time in nonliving environments. For example, Clostridium tetani survives in the soil and in the presence of oxygen as a resistant endospore. Although many viruses are soon destroyed once in contact with air, water, or other non-physiological conditions, certain types are capable of persisting outside of a living cell for varying amounts of time. For example, a study that looked at the ability of influenza viruses to infect a cell culture after varying amounts of time on a banknote showed survival times from 48 hours to 17 days, depending on how they were deposited on the banknote.[1] On the other hand, cold-causing rhinoviruses are somewhat fragile, typically surviving less than a day outside of physiological fluids.
A human acting as a reservoir of a pathogen may or may not be capable of transmitting the pathogen, depending on the stage of infection and the pathogen. To help prevent the spread of disease among school children, the CDC has developed guidelines based on the risk of transmission during the course of the disease. For example, children with chickenpox are considered contagious for five days from the start of the rash, whereas children with most gastrointestinal illnesses should be kept home for 24 hours after the symptoms disappear.
An individual capable of transmitting a pathogen without displaying symptoms is referred to as a carrier. A passive carrier is contaminated with the pathogen and can mechanically transmit it to another host; however, a passive carrier is not infected. For example, a health-care professional who fails to wash his hands after seeing a patient harboring an infectious agent could become a passive carrier, transmitting the pathogen to another patient who becomes infected.
By contrast, an active carrier is an infected individual who can transmit the disease to others. An active carrier may or may not exhibit signs or symptoms of infection. For example, active carriers may transmit the disease during the incubation period (before they show signs and symptoms) or the period of convalescence (after symptoms have subsided). Active carriers who do not present signs or symptoms of disease despite infection are called asymptomatic carriers. Pathogens such as hepatitis B virus, herpes simplex virus, and HIV are frequently transmitted by asymptomatic carriers. Mary Mallon, better known as Typhoid Mary, is a famous historical example of an asymptomatic carrier. An Irish immigrant, Mallon worked as a cook for households in and around New York City between 1900 and 1915. In each household, the residents developed typhoid fever (caused by Salmonella typhi) a few weeks after Mallon started working. Later investigations determined that Mallon was responsible for at least 122 cases of typhoid fever, five of which were fatal.[2]
A pathogen may have more than one living reservoir. In zoonotic diseases, animals act as reservoirs of human disease and transmit the infectious agent to humans through direct or indirect contact. In some cases, the disease also affects the animal, but in other cases the animal is asymptomatic.
![]()
- List some nonliving reservoirs for pathogens.
- Explain the difference between a passive carrier and an active carrier.
Transmission
Regardless of the reservoir, transmission must occur for an infection to spread. First, transmission from the reservoir to the individual must occur. Then, the individual must transmit the infectious agent to other susceptible individuals, either directly or indirectly. Pathogenic microorganisms employ diverse transmission mechanisms.
Contact Transmission
Contact transmission includes direct contact or indirect contact. Person-to-person transmission is a form of direct contact transmission. Here the agent is transmitted by physical contact between two individuals (Figure 12.9) through actions such as touching, kissing, sexual intercourse, or droplet sprays. Direct contact can be categorized as vertical, horizontal, or droplet transmission. Vertical direct contact transmission occurs when pathogens are transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding. Other kinds of direct contact transmission are called horizontal direct contact transmission. Often, contact between mucous membranes is required for entry of the pathogen into the new host, although skin-to-skin contact can lead to mucous membrane contact if the new host subsequently touches a mucous membrane. Contact transmission may also be site-specific; for example, some diseases can be transmitted by sexual contact but not by other forms of contact.
When an individual coughs or sneezes, small droplets of mucus that may contain pathogens are ejected. This leads to direct droplet transmission, which refers to droplet transmission of a pathogen to a new host over distances of one meter or less. A wide variety of diseases are transmitted by droplets, including influenza and many forms of pneumonia. Transmission over distances greater than one meter is called airborne transmission.
Indirect contact transmission involves inanimate objects called fomites that become contaminated by pathogens from an infected individual or reservoir (Figure 12.10). For example, an individual with the common cold may sneeze, causing droplets to land on a fomite such as a tablecloth or carpet, or the individual may wipe her nose and then transfer mucus to a fomite such as a doorknob or towel. Transmission occurs indirectly when a new susceptible host later touches the fomite and transfers the contaminated material to a susceptible portal of entry. Fomites can also include objects used in clinical settings that are not properly sterilized, such as syringes, needles, catheters, and surgical equipment. Pathogens transmitted indirectly via such fomites are a major cause of healthcare-associated infections (see Controlling Microbial Growth).


Vehicle Transmission
The term vehicle transmission refers to the transmission of pathogens through vehicles such as water, food, and air. Water contamination through poor sanitation methods leads to waterborne transmission of disease. Waterborne disease remains a serious problem in many regions throughout the world. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that contaminated drinking water is responsible for more than 500,000 deaths each year.[3] Similarly, food contaminated through poor handling or storage can lead to foodborne transmission of disease (Figure 12.11).
Dust and fine particles known as aerosols, which can float in the air, can carry pathogens and facilitate the airborne transmission of disease. For example, dust particles are the dominant mode of transmission of hantavirus to humans. Hantavirus is found in mouse feces, urine, and saliva, but when these substances dry, they can disintegrate into fine particles that can become airborne when disturbed; inhalation of these particles can lead to a serious and sometimes fatal respiratory infection.
Although droplet transmission over short distances is considered contact transmission as discussed above, longer distance transmission of droplets through the air is considered vehicle transmission. Unlike larger particles that drop quickly out of the air column, fine mucus droplets produced by coughs or sneezes can remain suspended for long periods of time, traveling considerable distances. In certain conditions, droplets desiccate quickly to produce a droplet nucleus that is capable of transmitting pathogens; air temperature and humidity can have an impact on effectiveness of airborne transmission.

Vector Transmission
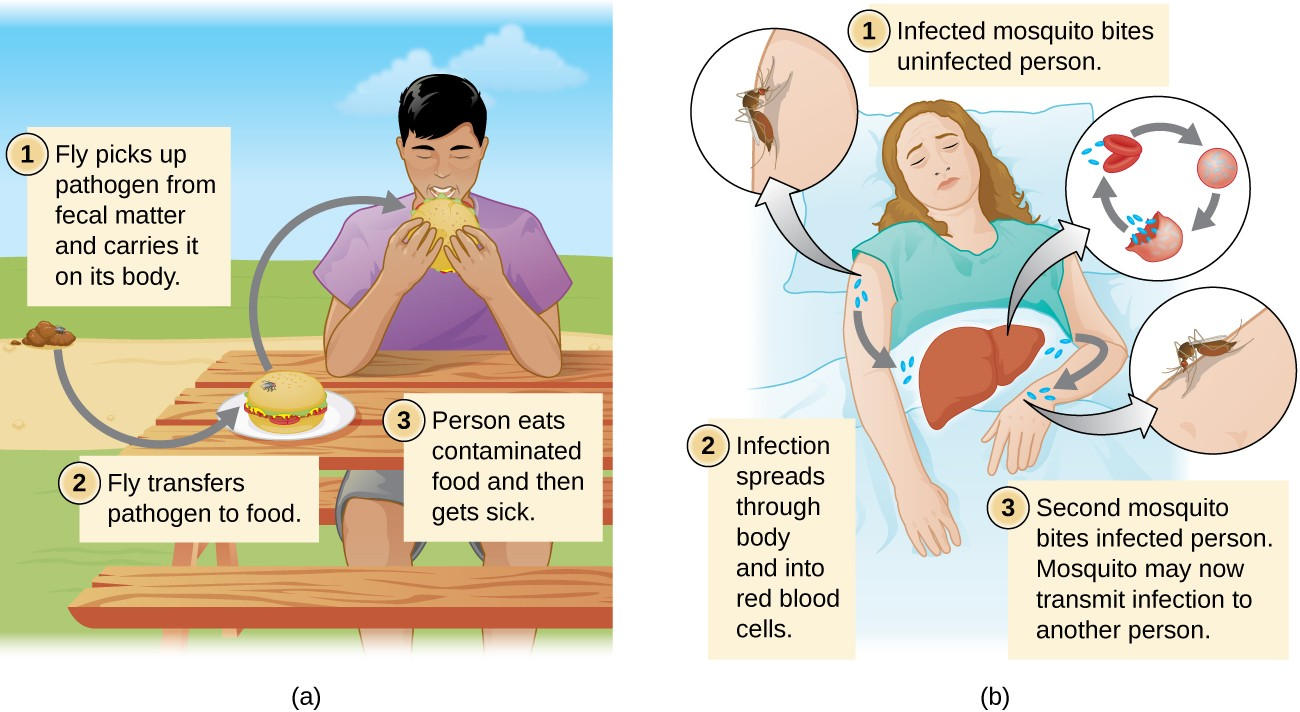
Diseases can also be transmitted by a mechanical or biological vector, an animal (typically an arthropod) that carries the disease from one host to another. Mechanical transmission is facilitated by a mechanical vector, an animal that carries a pathogen from one host to another without being infected itself. For example, a fly may land on fecal matter and later transmit bacteria from the feces to food that it lands on; a human eating the food may then become infected by the bacteria, resulting in a case of diarrhea or dysentery (Figure 12.12).
Biological transmission occurs when the pathogen reproduces within a biological vector that transmits the pathogen from one host to another (Figure 12.12). Arthropods are the main vectors responsible for biological transmission (Figure 12.12). Most arthropod vectors transmit the pathogen by biting the host, creating a wound that serves as a portal of entry. The pathogen may go through part of its reproductive cycle in the gut or salivary glands of the arthropod to facilitate its transmission through the bite. For example, hemipterans (called “kissing bugs” or “assassin bugs”) transmit Chagas disease to humans by defecating when they bite, after which the human scratches or rubs the infected feces into a mucous membrane or break in the skin.
Biological insect vectors include mosquitoes, which transmit malaria and other diseases, and lice, which transmit typhus. Other arthropod vectors can include arachnids, primarily ticks, which transmit Lyme disease and other diseases, and mites, which transmit scrub typhus and rickettsial pox. Biological transmission, because it involves survival and reproduction within a parasitized vector, complicates the biology of the pathogen and its transmission. There are also important non-arthropod vectors of disease, including mammals and birds. Various species of mammals can transmit rabies to humans, usually by means of a bite that transmits the rabies virus. Chickens and other domestic poultry can transmit avian influenza to humans through direct or indirect contact with avian influenza virus A shed in the birds’ saliva, mucous, and feces.
![]()
- Describe how diseases can be transmitted through the air.
- Explain the difference between a mechanical vector and a biological vector.
Quarantining
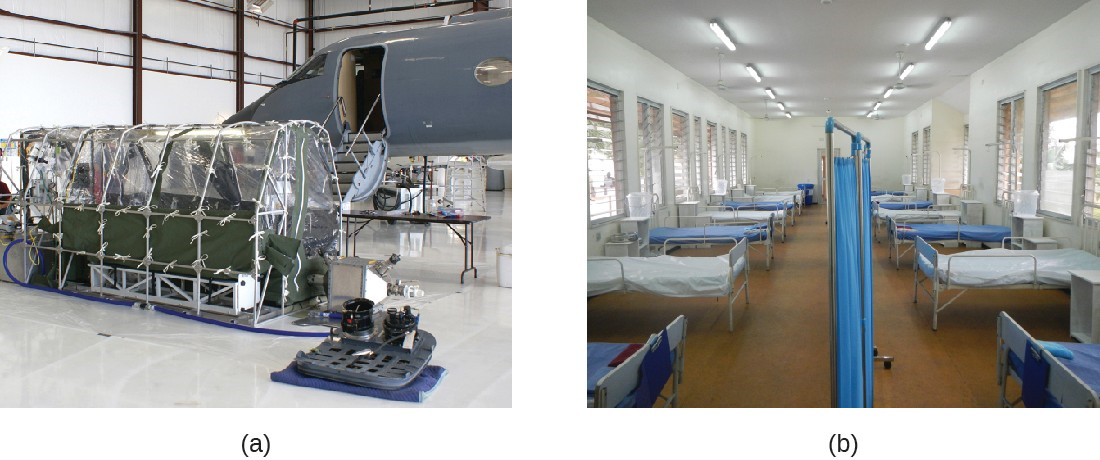
Individuals suspected or known to have been exposed to certain contagious pathogens may be quarantined, or isolated to prevent transmission of the disease to others. Hospitals and other health-care facilities generally set up special wards to isolate patients with particularly hazardous diseases such as tuberculosis or Ebola (Figure 12.13). Depending on the setting, these wards may be equipped with special air-handling methods, and personnel may implement special protocols to limit the risk of transmission, such as personal protective equipment or the use of chemical disinfectant sprays upon entry and exit of medical personnel.
The duration of the quarantine depends on factors such as the incubation period of the disease and the evidence suggestive of an infection. The patient may be released if signs and symptoms fail to materialize when expected or if preventive treatment can be administered in order to limit the risk of transmission. If the infection is confirmed, the patient may be compelled to remain in isolation until the disease is no longer considered contagious.
In the United States, public health authorities may only quarantine patients for certain diseases, such as cholera, diphtheria, infectious tuberculosis, and strains of influenza capable of causing a pandemic. Individuals entering the United States or moving between states may be quarantined by the CDC if they are suspected of having been exposed to one of these diseases. Although the CDC routinely monitors entry points to the United States for crew or passengers displaying illness, quarantine is rarely implemented.

Healthcare-Associated (Nosocomial) Infections
Hospitals, retirement homes, and prisons attract the attention of epidemiologists because these settings are associated with increased incidence of certain diseases. Higher rates of transmission may be caused by characteristics of the environment itself, characteristics of the population, or both. Consequently, special efforts must be taken to limit the risks of infection in these settings.
Infections acquired in health-care facilities, including hospitals, are called nosocomial infections or healthcare- associated infections (HAI). HAIs are often connected with surgery or other invasive procedures that provide the pathogen with access to the portal of infection. For an infection to be classified as an HAI, the patient must have been admitted to the health-care facility for a reason other than the infection. In these settings, patients suffering from primary disease are often afflicted with compromised immunity and are more susceptible to secondary infection and opportunistic pathogens.
In 2011, more than 720,000 HAIs occurred in hospitals in the United States, according to the CDC. About 22% of these HAIs occurred at a surgical site, and cases of pneumonia accounted for another 22%; urinary tract infections accounted for an additional 13%, and primary bloodstream infections 10%.[4] Such HAIs often occur when pathogens are introduced to patients’ bodies through contaminated surgical or medical equipment, such as catheters and respiratory ventilators. Health-care facilities seek to limit nosocomial infections through training and hygiene protocols such as those described in Control of Microbial Growth.

- Give some reasons why HAIs occur.
- Yves Thomas, Guido Vogel, Werner Wunderli, Patricia Suter, Mark Witschi, Daniel Koch, Caroline Tapparel, and Laurent Kaiser. “Survival of Influenza Virus on Banknotes.” Applied and Environmental Microbiology 74, no. 10 (2008): 3002–3007. ↵
- Filio Marineli, Gregory Tsoucalas, Marianna Karamanou, and George Androutsos. “Mary Mallon (1869–1938) and the History of Typhoid Fever.” Annals of Gastroenterology 26 (2013): 132–134. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3959940/pdf/ AnnGastroenterol-26-132.pdf. ↵
- World Health Organization. Fact sheet No. 391—Drinking Water. June 2005. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs391/en. ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “HAI Data and Statistics.” 2016. http://www.cdc.gov/hai/surveillance. Accessed Jan 2, 2016 ↵

